FIGURE 5.
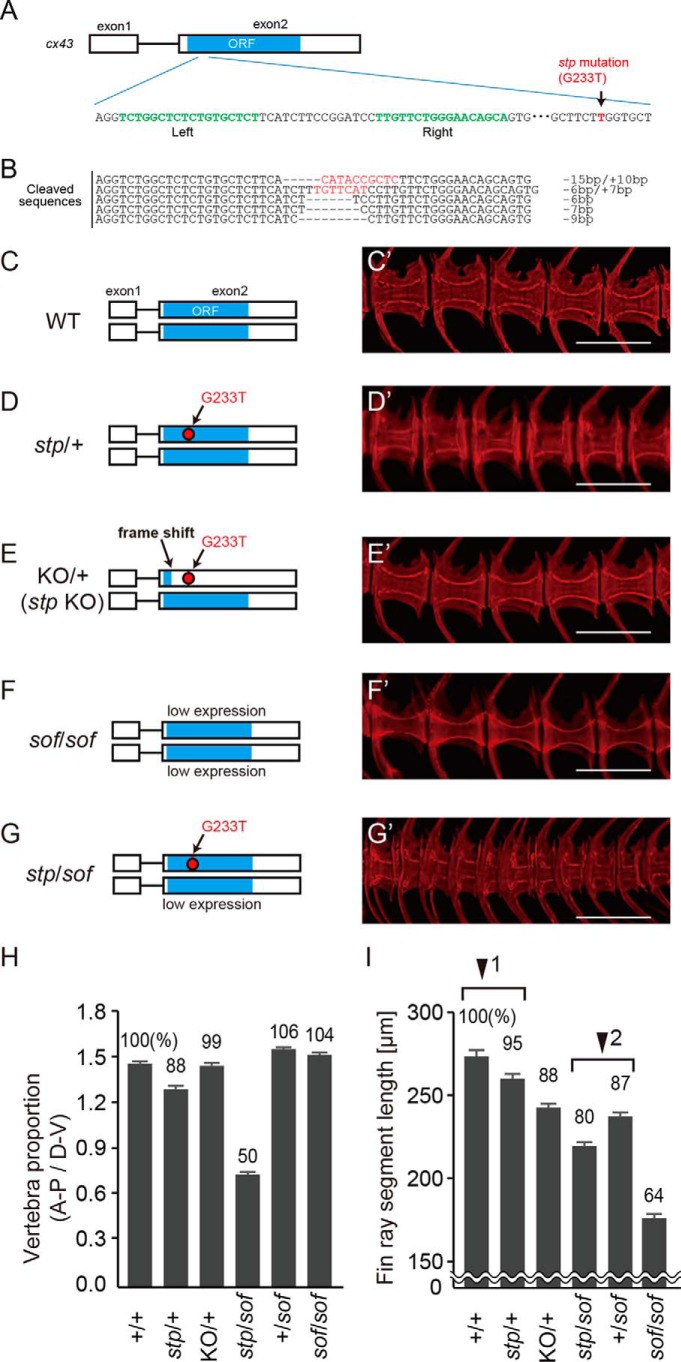
Vertebral and fin ray segment phenotypes of zebrafish mutants. A and B, knock out of cx43stp by TALEN. A, schematic of cx43 gene structure. The green letters are the DNA binding sites by TALEN. The red letter is the stp mutation (G233T). B, Mutated sequences produced by TALEN. Three F1 lines had frame-shifting mutations, which were (−15 bp/+10 bp), (−6 bp/+7 bp), and (−7 bp). The (−15 bp/+10 bp) line was used for the stp gene knock-out investigation. C–G, vertebral structure of wild type (C), stp/+ (D), KO/+ (stp allele knock-out) (E), sofb123/b123 (F), and stp/sofb123 (G) fish. Cleared, alizarin red S-stained specimens were made from 70 dpf fishes. KO/+ fish had a wild type allele and a knock-out stp allele. sofb123/b123 fish showed normal vertebra structure, but stp/sofb123 fish had markedly shorter vertebrae. H and I, six mutant fish were randomly chosen and compared with six of their wild type siblings at 70 dpf. H, length to height ratio of vertebral centrums. I, length of fin ray segment. The segments second from the tail bud were measured, and average length was calculated. Arrowheads 1 and 2 indicate pairs of fish genotypes that differ in the presence or absence of the stp allele. Error bars, S.E. Scale bars, 500 μm in C′–G′. stp/+, stptl28d/+; sof/sof, sofb123/b123; stp/sof, stp/sofb123.