Figure 3.
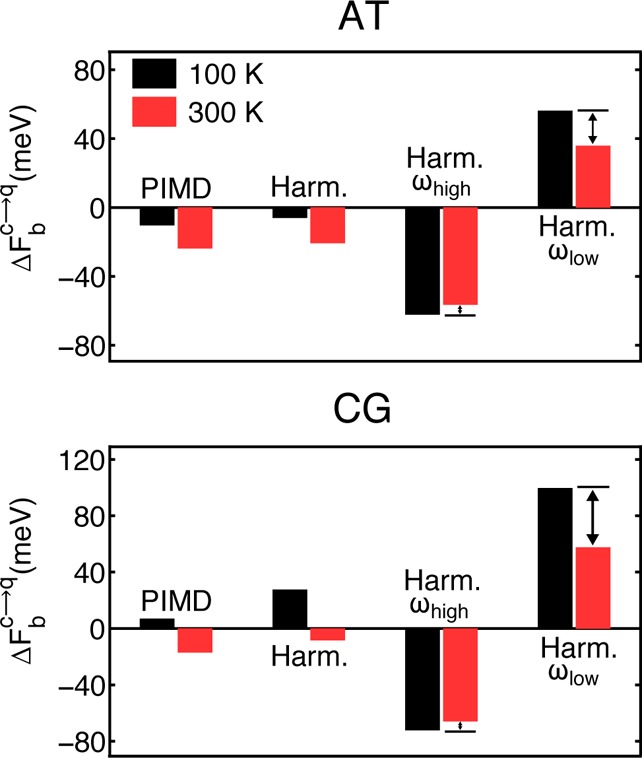
Competing quantum effects and explanation of the anomalous temperature dependence. The binding free energy change (ΔFbc→q) obtained from the PIMD simulations is compared with results from the harmonic approximation (Harm.). The binding free energy changes within the harmonic approximation are also decomposed into high- (ωhigh) and low-frequency (ωlow) contributions, revealing that the net change in binding free energy arises from a significant cancellation of contributions from these two regimes. The unusual temperature dependence simply arises because of a greater cancellation of terms at 100 K (black bars) than at 300 K (red bars). The change with temperature is more pronounced for the contribution from the low-frequency modes than it is for the high-frequency modes.
