Figure 4.
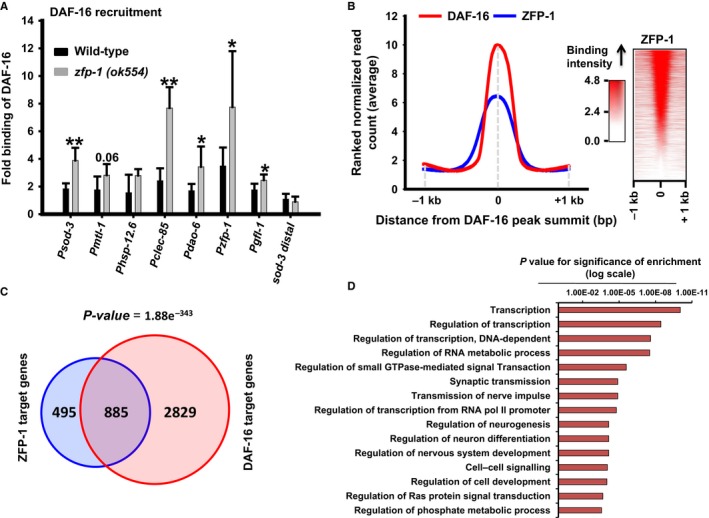
ZFP‐1 influences DAF‐16/FOXO recruitment to its target promoters. (A) ChIP‐PCR to determine DAF‐16 recruitment to different target promoters in WT and zfp‐1(ok554). Binding in WT /zfp‐1(ok554) is normalized to that of daf‐16(‐). Recruitment at a distal region of sod‐3 is taken as control. The graph is plotted from three experiments. Error bars represent standard deviation. **P ≤ 0.01; *P ≤ 0.05 by Student's t‐test. (B) Distribution of ZFP‐1 peaks with respect to DAF‐16/FOXO binding summits as determined by ChIP‐seq experiments (left panel). Distribution of ZFP‐1 reads with respect to DAF‐16 binding summit across all chromosomes (right panel). ZFP‐1 ChIP‐seq data from MODENCODE were reanalysed using our bioinformatic pipeline. (C) Overlap of ZFP‐1 and DAF‐16 direct target genes as determined by ChIP‐seq experiments. (D) Gene Ontology (GO) term analysis of common target genes of DAF‐16/FOXO and ZFP‐1. Only top 15 GO terms that were enriched are shown.
