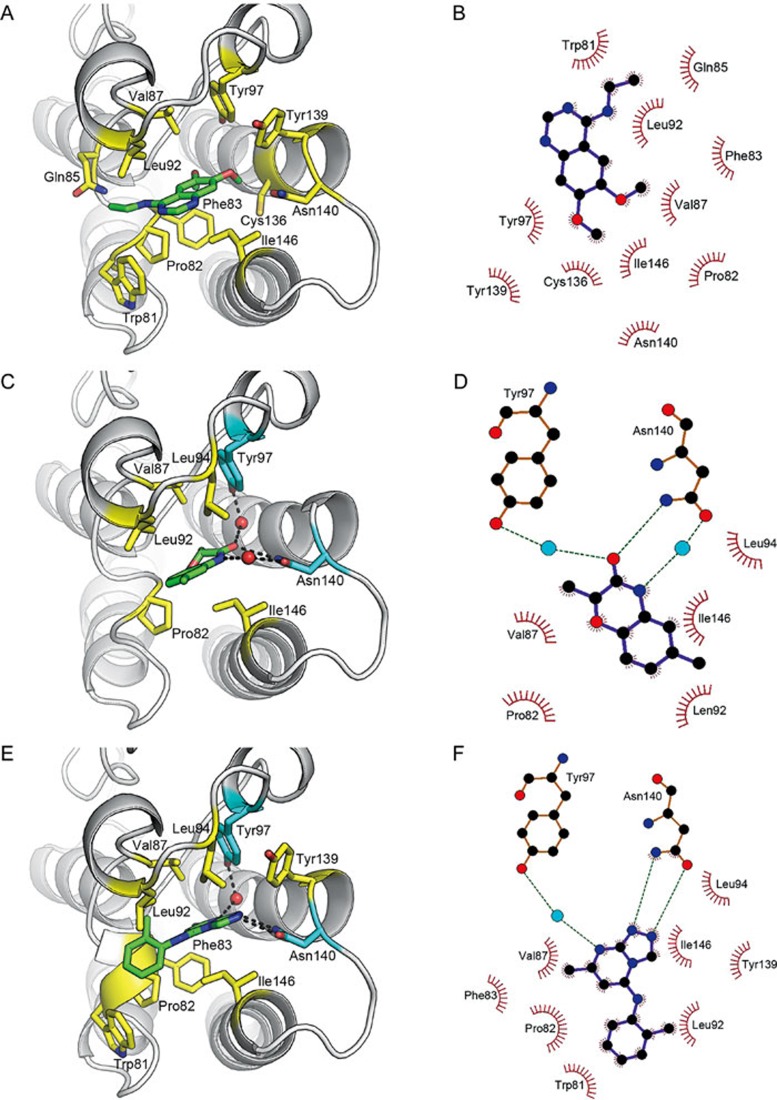
Figure 5.
Expanded view of BRD4(I)-hit compound co-crystal structures and schematic diagrams of BRD4(I)-hit compound interactions. (A) Expanded view of BRD4(I) bound to hit compound 1. (B) Schematic diagram of BRD4(I)-hit compound 1 interactions. Extensive hydrophobic interactions form between BRD4(I) and hit compound 1, and the involved residues in BRD4(I) and the atoms in hit compound 1 are highlighted with spiked lines. (C) Expanded view of BRD4(I) bound to hit compound 6. (D) Schematic diagram of BRD4(I)-hit compound 6 interactions. The residues in BRD4(I) and the atoms in hit compound 6, which are involved in the hydrophobic interaction network of these two molecules, are highlighted with spiked lines. The hydrogen bonds are highlighted with green dashed lines, and the blue spheres represent water molecules. (E) Expanded view of BRD4(I) bound to hit compound 9. (F) Schematic diagram of BRD4(I)-hit compound 9 interactions. The residues in BRD4(I) and the atoms in hit compound 9, which are involved in the hydrophobic interaction network of these two molecules, are highlighted with spiked lines. The hydrogen bonds are highlighted with green dashed lines, and the blue spheres represent water molecules.