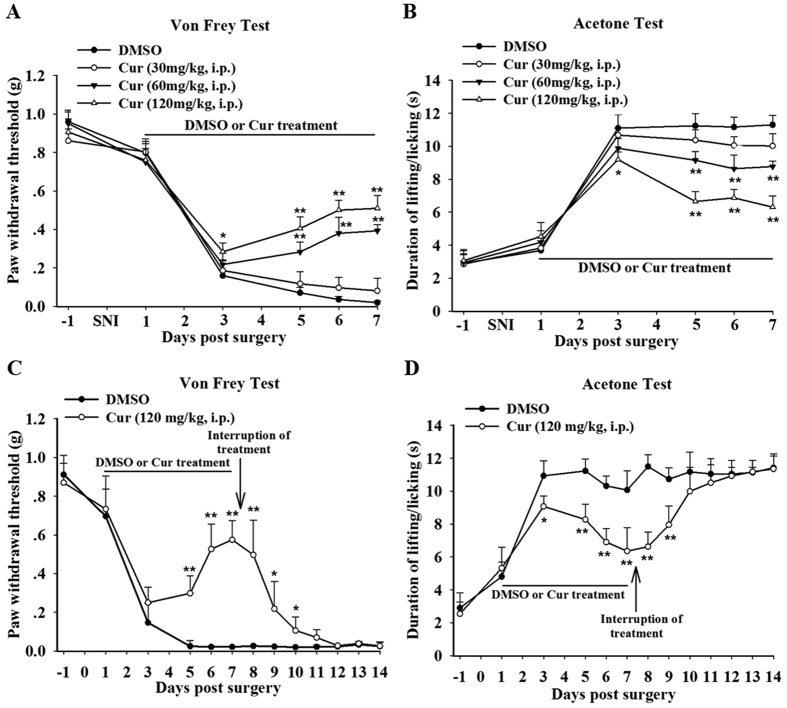
Figure 1. Anti-allodynic effect of curcumin on SNI-induced neuropathic pain.
Time course showing the changes in the mechanical withdrawal threshold in the Von Frey test (A) and the duration of lifting/licking in the acetone test (B) in the ipsilateral hind paw of mice chronically intraperitoneal (i.p) treated with vehicle (20% DMSO) or curcumin (30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg, or 120 mg/kg). Treatment started on day 1 after SNI and was administered twice a day until day 7. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the DMSO treatment group; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test; n = 8 per group. (C,D) Effect of curcumin treatment (120 mg/kg, i.p) on the response to mechanical or cold stimuli in SNI mice. The administration of vehicle or curcumin was stopped after 7 days of repeated treatment. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the DMSO group; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test; n = 8 per group. Cur = curcumin. All of the data are shown as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).