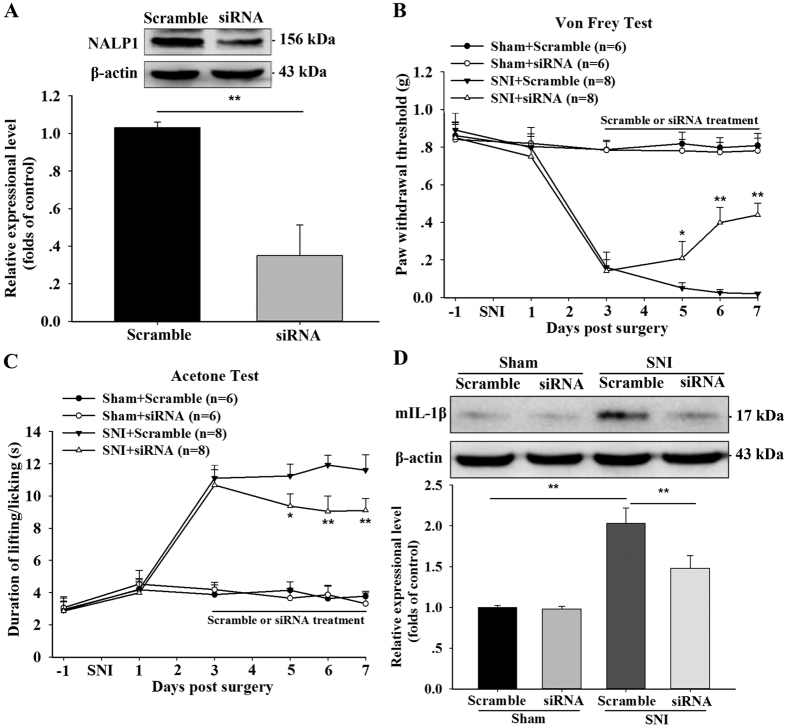
Figure 3. Role of spinal NALP1 in SNI-induced neuropathic pain.
(A) Immunoblotting showed that the small interfering RNA against NALP1 (siRNA) (5 μg), but not the scrambled control (Scramble), reduced NALP1 protein levels in the spinal cords dissected from SNI mice on day 7 after behaviour analysis. Cropped gels/blots are used in this figure and the immunoblots were obtained from the microgel running in the same experimental conditions. **p < 0.01; student’s t test; n = 4 per group. (B,C) Time course of the effect of NALP1 siRNA on SNI-induced mechanical and cold allodynia. The repeated intrathecal injection of siRNA targeting NALP1 (5 μg), but not scrambled siRNA, from day 3 to day 7 after SNI, facilitated recovery from SNI-induced mechanical and cold allodynia. siRNA administration did not affect the baseline of mechanical threshold and lifting latency in sham mice. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the SNI + scrambled group; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test; n = 8 per group. (D) 5 μg NALP1 siRNA, but not scrambled siRNA, significantly reversed the SNI-induced up-regulation of mature IL-1β as determined by western blotting. Cropped gels/blots are used in this figure and the immunoblots were obtained from the microgel running in the same experimental conditions. **p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test; n = 4 per group. All of the data are shown as the mean ± SEM.