Figure 2.
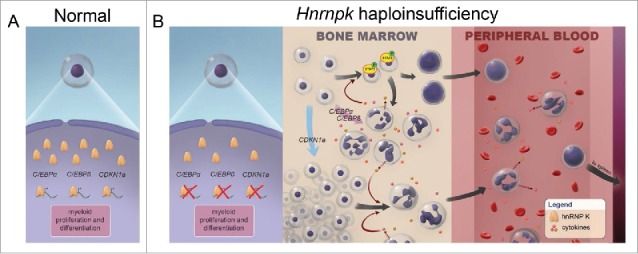
Hnrnpk haploinsufficiency results in proliferative and differentiation defects in the haematopoietic compartment. A. Under normal conditions, hnRNP K is required to maintain a homeostatic balance in haematopoietic development through its regulation of p21, C/EBP-αand β. B. (Left) Hnrnpk haploinsufficiency results in reduced hnRNP K expression and diminished p21, C/EBP-α and β levels. (Middle) In the bone marrow, reduced hnRNP K allows for expansion of the haematopoietic compartment, increased cytokine expression, and activation of Stat-3 signaling. (Right) Cells from the hyperproliferative bone marrow are mobilized and extravasate from the marrow into the periphery.
