Figure 3.
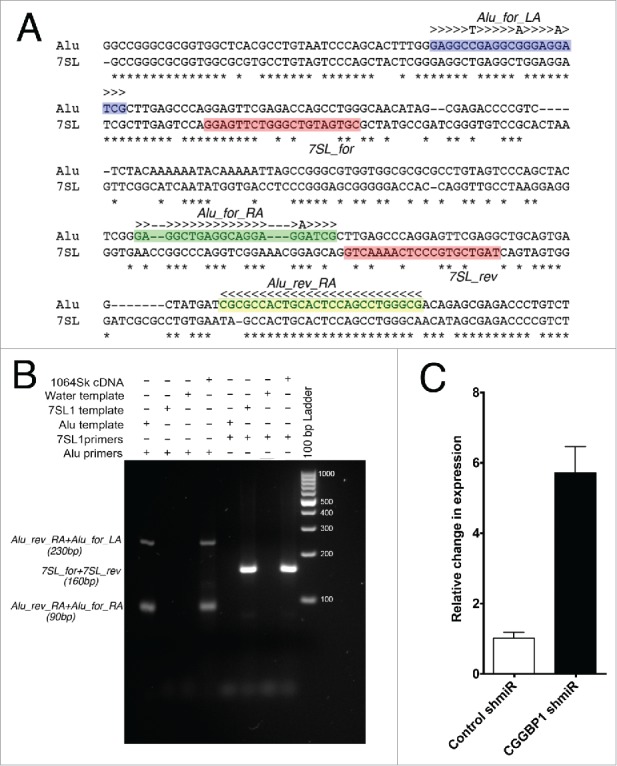
Alu and 7SL PCR primers, test of specificity and quantitation of Alu RNA. (A) Location of primers: Alu_rev_RA (yellow shade) will amplify a 90 bp fragment with Alu_for_RA (Alu forward primer annealing in right arm, green shade) and a 230 bp fragment with Alu_for_LA (Alu forward primer annealing in left arm, blue shade). The 2 7SL primers (7SL_for and 7SL_rev; pink shade) will amplify a 160 bp fragment. Poor sequence complementarity between 7SL primers and Alu consensus sequence ensures no Alu amplification by 7SL primers. Alu_rev_RA primer has been extended by 3 bases at the 3′ end (rest of the sequence the same as described by Marullo et al., 2010) to generate terminal mismatch between Alu_rev_RA primer and 7SL template. This prevent cross amplification of 7SL by Alu primers. (B) By using cDNA as a general template, purified 90 and 160 bps Alu fragments as Alu template and annealed oligos of 7SL1 sequence as 7SL-specific template (see methods for sequence), the specificity of the primers was confirmed. (C) qPCRs show that CGGBP1 depletion by CGGBP1 shmiR induced Alu RNA levels as compared to control shmiR (P < .0001; n = 3). Y-axis values are obtained from subtraction of Ct values of an all-sample-mix as an internal standard from the Ct values of each sample and the difference subjected to negative power of base 2. The values were then normalized to set control (Stimulated) to a mean of 1.
