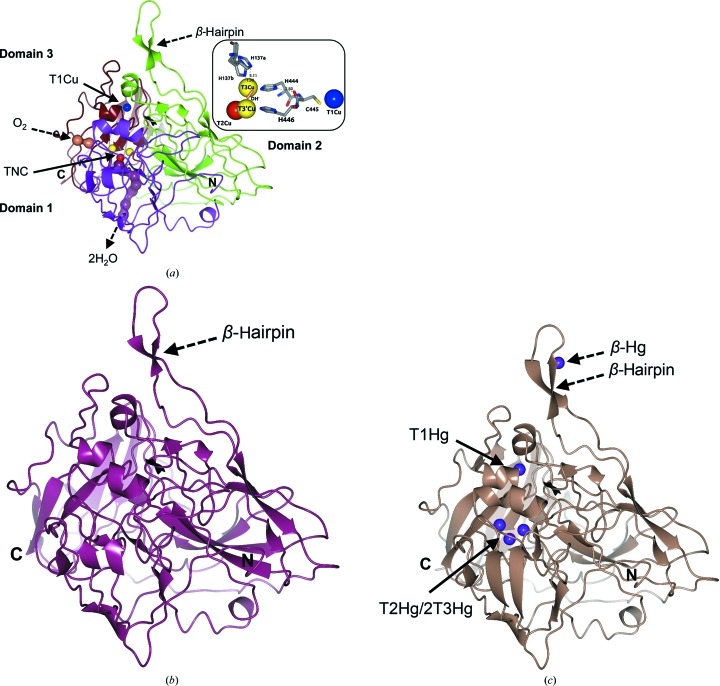
Figure 3.
Crystallographic structures of Tth-MCO in holo, apo and Hg-bound states. (a) High-resolution structure of Tth-MCO showing the cupredoxin-domain organization (domain 1, magenta; domain 2, green; domain 3, brown) with T1Cu (blue sphere) located in domain 3 and the TNC (T2Cu, red sphere; binuclear T3Cu–T3′Cu cluster, yellow spheres) placed at the interface between domains 1 and 3. The molecular oxygen-entrance channel (coral) towards T3Cu and the water-molecule exit channel (dark purple) from T2Cu are represented by water molecules found in the Tth-MCO structure. Right inset, close-up of four catalytic Cu atoms of Tth-MCO, the hydroxide ligand (coral cylinder) bridging the binuclear T3Cu–T3′Cu cluster and the electron-transfer pathway from T1Cu to the TNC. (b, c) Two inactive forms of Tth-MCO: (b) apo Tth-MCO (dark purple) and (c) Hg-Tth-MCO-2h (pale brown) with Hg bound (purple spheres) instead of Cu. It is notable that a fifth Hg-binding site (β-Hg) was observed in (c). Distances are in Å.