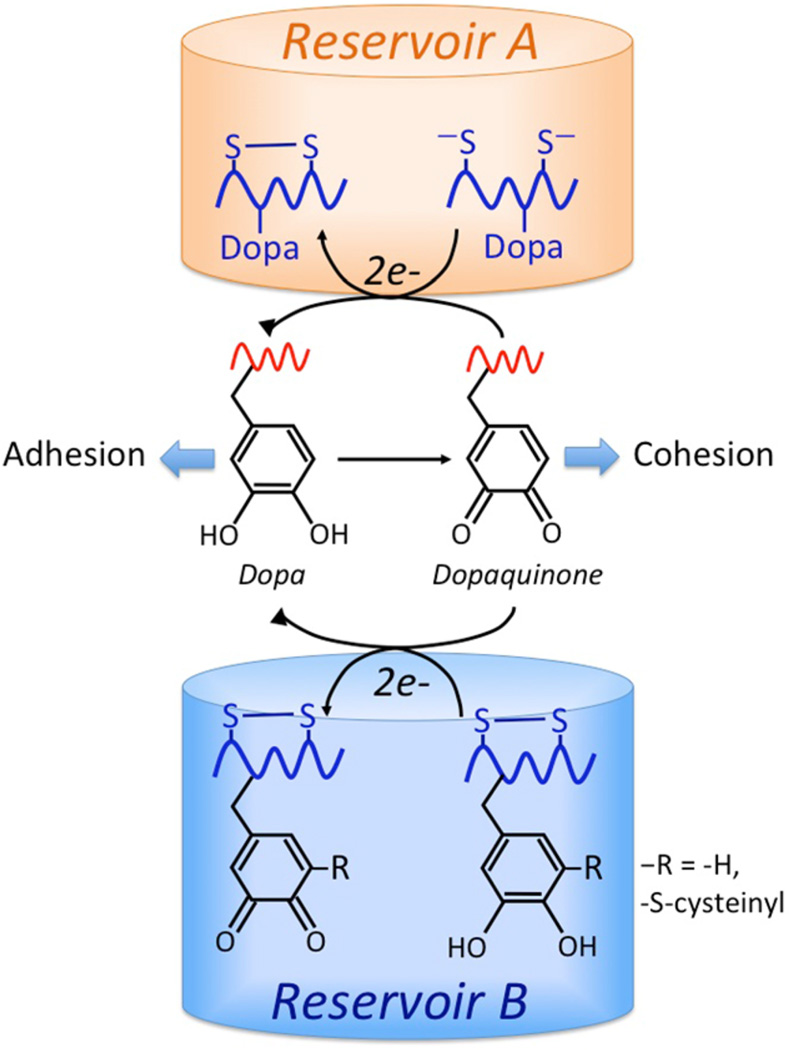
Figure 6.
Reducing reservoirs in Mfp-6 that maintain DOPA-containing adhesive proteins Mfp-3 and Mfp-5 during surface deposition. The reduced form of DOPA is required for the first, bidentate adsorption step of adhesion, whereas the oxidized form (Dopaquinone) contributes to the covalent pathways of cohesion, e.g., aryl coupling and Michael additions. Reservoir A consists of 9 equiv of thiolate Cys residues/Mfp-6 that provides strongly reducing electrons (9e− + 9H+). Reservoir B, in contrast, consists of 4–5 equiv of DOPA/Mfp-6 that provides weakly reducing electrons (8–10e− + 8–10H+). There may be electron shuttling between the two populations.