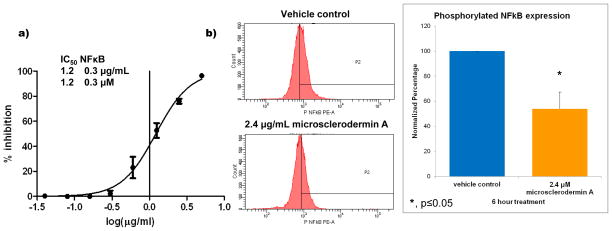
Figure 2. Inhibition of NFκB by microsclerodermin A.
a) Serial dilutions of the compound in the screening assay and subsequent non-linear regression analysis showed that the concentration of microsclerodermin A required to obtain 50% inhibition (IC50) of NFκB activity in the reporter assay was 1.2 μM with a standard deviation of 0.3 μM. b) Significant inhibition of NFκB was also observed in AsPC-1 pancreatic cancer cells treated with 2X the IC50 for 6 hours as analyzed by flow cytometry for the phosphorylated form of NFκB (Ser 529). One representative histogram shown; gates were set up against isotype control. Graphical representation of the flow cytometry data normalized to vehicle control shows the average of 3 experiments ± standard deviation. Statistical significance was determined through a student’s T test.