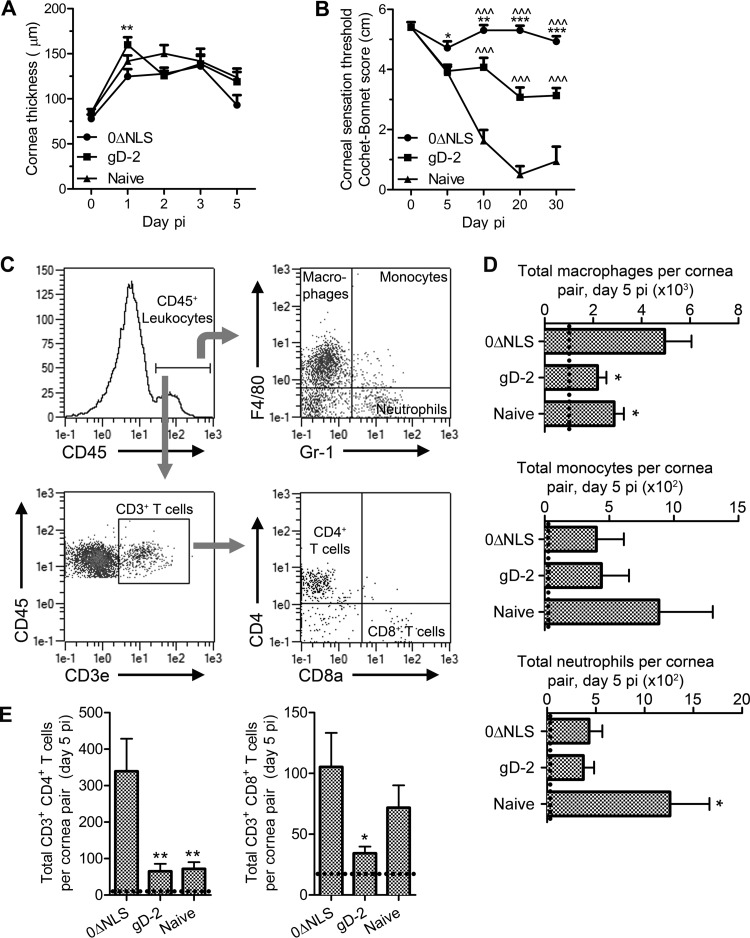
FIG 3.
Vaccine-mediated protection from corneal pathology. (A) Central corneal thickness was evaluated via ultrasound pachymetry to assess corneal edema during the early acute phase post-HSV-1 challenge in immunized and naive mice (n = 10 to 20 corneas/group/time point; 2 to 3 independent experiments). (B) Central corneal sensation was measured longitudinally by Cochet-Bonnet esthesiometry in immunized and naive mice as a functional measure of vaccine-mediated protection from corneal denervation following HSV-1 infection (n = 10 to 30 corneas/group/time point; 4 independent experiments). For panels A and B, two-way ANOVAs with Bonferroni posttests were utilized to determine statistical differences. (C) Representative composite depicting gating strategy for flow cytometric analysis of cornea-infiltrating leukocytes. (D) Quantification of cornea-infiltrating myeloid cells, including macrophages (F4/80+ Gr-1−), monocytes (F4/80+ Gr-1+), and neutrophils (F4/80− Gr-1+). (E) Quantification of cornea-infiltrating CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets. For panels D and E, n = 10 to 15 mice/group with 4 to 5 independent experiments; dashed lines indicate average values for uninfected controls (n = 2). Differences in cell populations were determined by one-way ANOVA with Student-Newman-Keuls multiple comparison tests. Significance thresholds for all panels are indicated as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***/^^^, P < 0.001. Significant differences in results relative to the gD-2-immunized and naive groups are shown as asterisks and carets, respectively.