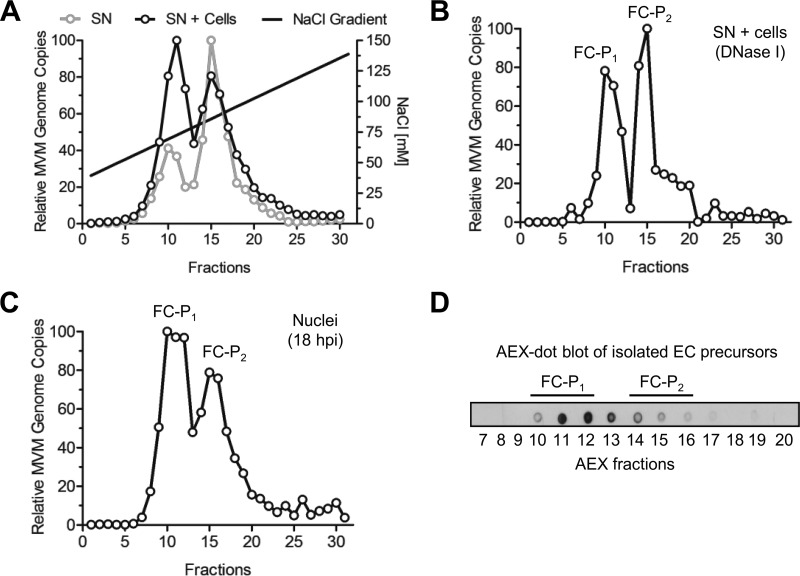
FIG 1.
Isolation of two distinct populations of progeny DNA-containing particles. (A) Progeny viruses (1010 DNA-containing particles) were collected from the culture media of infected A9 monolayers (supernatant [SN]) after extensive cytopathic effect (8 dpi). Alternatively, the medium was enriched with additional intracellular particles by repeated freeze-thaw cycles (SN + cells). AEX was performed, and fractions were collected. The DNA-containing particles in each fraction were quantified by qPCR. (B) Prior to AEX-qPCR, the virus progeny (SN + cells) was treated with DNase I. (C) A9 cells (3 × 106) were infected at a multiplicity of infection of 5,000 DNA-containing particles per cell for 1 h at 4°C and were then washed to remove unbound virus. The cells were further incubated at 37°C for 18 h. To avoid reinfection, neuraminidase and an anti-capsid MAb were added to the cells. Nuclei were purified, and the nuclear progeny was analyzed by AEX-qPCR. (D) EC isolated from infected A9 cells (8 dpi) were subjected to AEX followed by dot blot analysis using the anti-capsid MAb for detection.