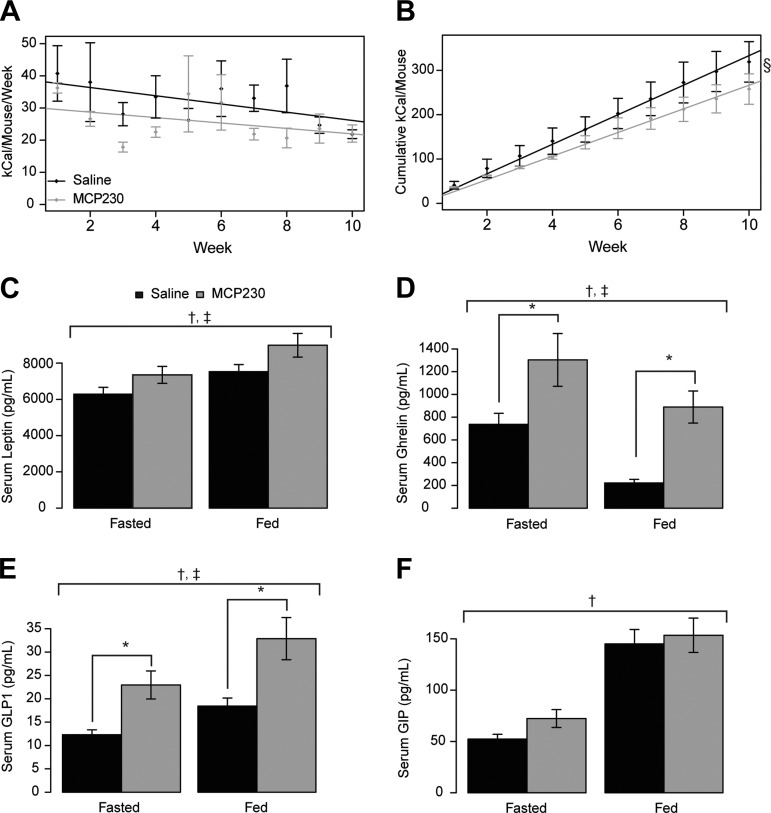
Fig. 2.
Gestational exposure to MCP230 causes a reduction in food intake and alters “hunger hormone” concentrations on a high-fat diet. A and B: food intake per mouse was calculated on a weekly (A) and cumulative (B) basis throughout the high-fat diet phase of the intervention. C–E: MCP230-exposed mice had elevated serum concentrations of leptin (C), ghrelin (D), and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1; E) after access to the high-fat diet. F: serum glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) tended to be elevated during the fasted state, although this did not attain statistical significance. Fed serum was collected at ZT12. Fasting serum was collected following an overnight fast (∼16 h) at ZT4. Data shown are group means ± SE; n = 8–14/group. §P < 0.05 by mixed linear model, compared by χ2 test (B); †main effect for feeding state (C–F); ‡main effect for MCP230 exposure by 2-way ANOVA (C–E); *P < 0.05 via a Wilcoxon rank sum test (D and E). Black bars, saline-exposed mice; gray bars, MCP230-exposed mice.