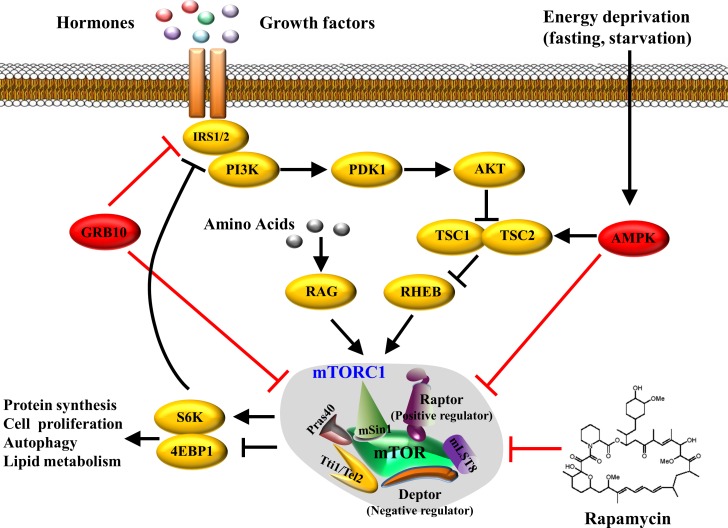
Fig. 1.
Mammalian or mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling pathway. The mTORC1 activate can be induced by hormones and growth factors (e.g., insulin, IGF-I, etc.) through a PI3K/Akt-mediated pathway, and by amino acids (mainly leucine) through Rag GTPases. On the other hand, activation of mTORC1 can be suppressed by rapamycin, mTORC1 downstream substrate Grb10, and energy deprivation-induced AMPK activation. Activated mTORC1 subsequently activates downstream S6K or inhibits 4E-BP1, resulting in protein translation, cellular proliferation, autophagy, or lipid metabolism.