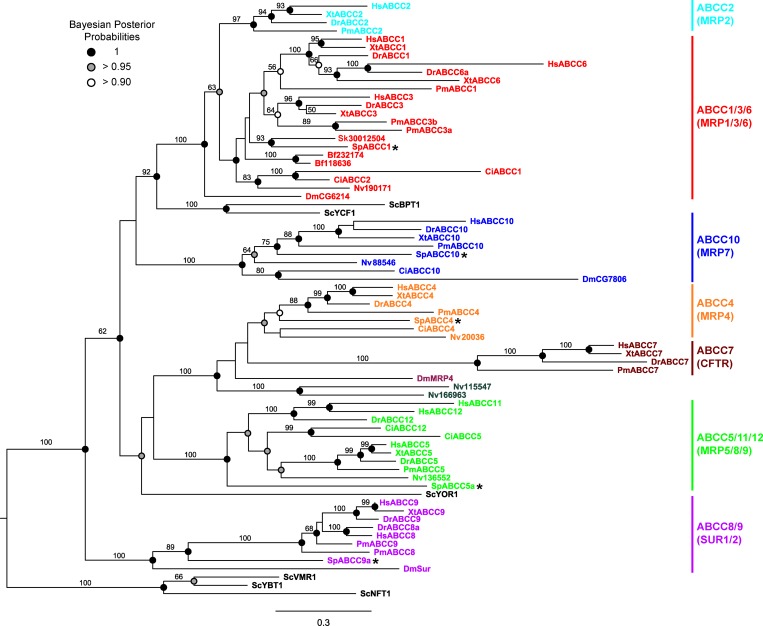
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic relationships of ATP-binding cassette C subfamily (ABCC) transporters of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (Sp) with human (Hs), Xenopus tropicalis (Xt), Danio rerio (Dr), Petromyzon marinus (Pm), Ciona intestinalis (Ci), Branchiostoma floridae (Bf), Saccoglossus kowalevskii (Sk), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm), Nematostella vectensis (Nv), and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc). The sea urchin efflux transporter SpABCC1 clusters in a well-supported clade containing ABCC1-ABCC2-ABCC3-ABCC6 from vertebrates and single ABCC proteins or likely lineage-specific paralogs from other invertebrates (Ci, Bf, Sk, Nv, and Dm). SpABCC1 is co-orthologous to vertebrate ABCC1-ABCC3-ABCC6 transporters. The sea urchin also has orthologs to ABCC4 and ABCC10 and a co-ortholog to ABCC5-ABCC11-ABCC12 and ABCC8-ABCC9 clades in vertebrates. The maximum-likelihood phylogeny is presented with posterior probability (>0.9) and maximum-likelihood bootstraps (>50%) indicated for each branch.