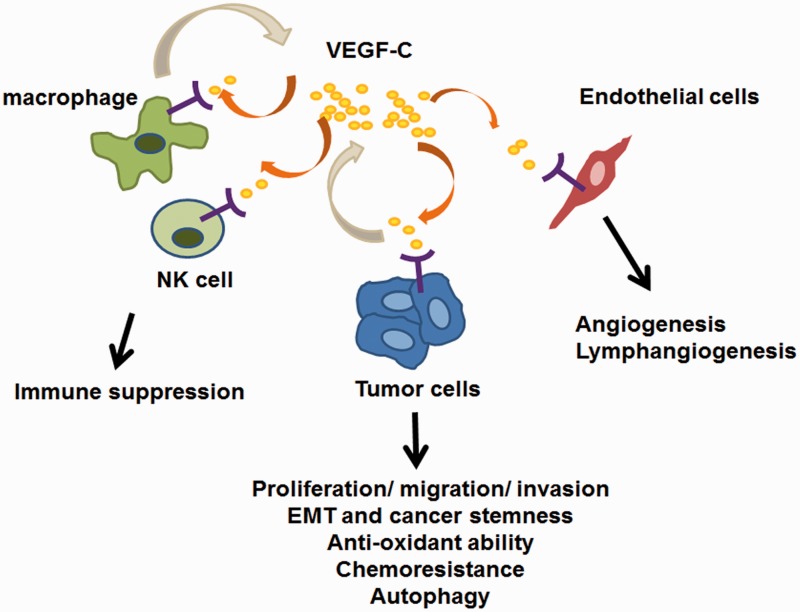
Figure 1.
Multiple functions of VEGF-C in tumor progression. VEGF-C binds to receptors expressed on endothelial cells and promotes angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Tumor cells which express VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, and NRP2 can receive VEGF-C autocrine signals and trigger downstream pathway which mediates aggressive phenotypes. Tumor-associated macrophages are another source of VEGF-C which contributes to the increased expression of VEGF-C in the microenvironment. Immune cells, such as NK cells, can receive VEGF-C signal and thus exhibit immune suppressive functions which favor tumor progression. VEGF-C: vascular endothelial growth factor-C. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)