Figure 2.
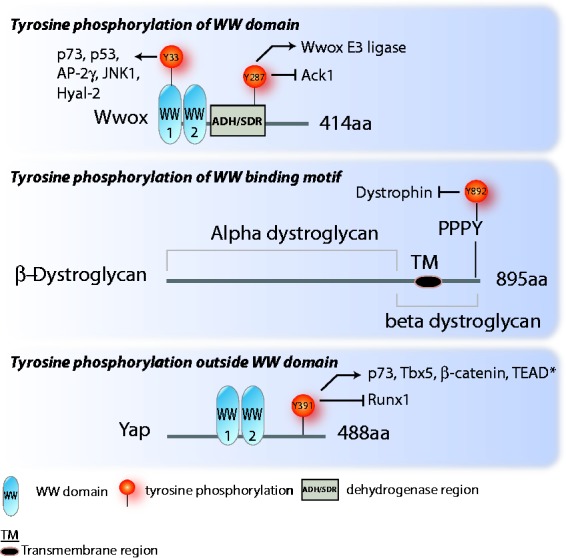
Schematic representation of WWox, β-dystroglycan, and Yap. These three proteins serve as examples for three ways tyrosine phosphorylation can affect WW domain interaction: (1) phosphorylation of the WW domain itself, as seen in Wwox; (2) phosphorylation of the WW binding domain, as seen in β-dystroglycan; and (3) phosphorylation outside of the WW domain that affects WW domain interactions, as seen with Yap. The Y391 site is the same as Y357 in Yap1, the isoform with one WW domain. The protein interactions affected by the phosphorylation are indicated by an arrow for increased interaction due to the phosphorylation, and a blunted arrow for decreased interaction. *The effect of Yap Y391 phosphorylation on Yap/TEAD interaction and activity may be different in different contexts. Tamm et al.33 showed that Yes phosphorylation of Yap increased association with and activation of TEAD. It should be noted, however, that in this work the Yap phosphorylation site was not specifically characterized. Keshet et al.68 showed that Yap Y391 phosphorylation reduced Yap coactivation of TEAD, but it did not reduce Yap-TEAD binding. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)
