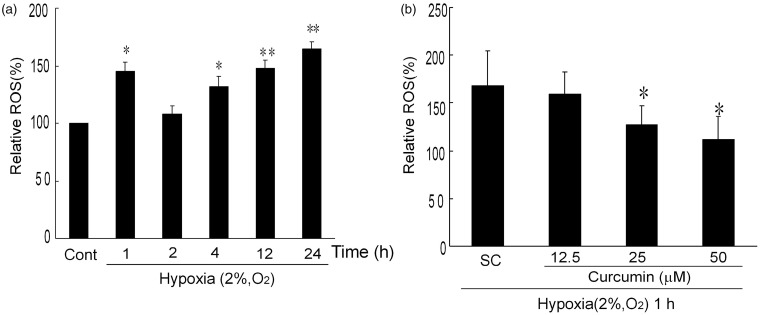
Figure 7.
Curcumin inhibits hypoxia-induced ROS in K1 cells. (a) Time-dependent effects of hypoxia-induced ROS in K1 cells. K1 cells were exposed to hypoxia for indicated times (2% O2, v/v), subsequently, cells were stained with DCFA-DH (10 µmol/L) for 20 min and analyzed with flow cytometry. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus control (Student’s two-tailed t-test). (b) Effects of curcumin on hypoxia-induced ROS in K1 cells. K1 cells were exposed to various concentrations of curcumin (0, 12.5, 25, and 50 µmol/L) for 1 h. Then the cells underwent hypoxia (2% O2, v/v) for 1 h. After pretreatment, the cells were detected by DCFA-DH. All of the data were expressed as the mean ± SEM. of the three experiments and each included triplicate sets. Cont: control, SC: solvent control. *P < 0.05 versus SC (Student’s two-tailed t-test)