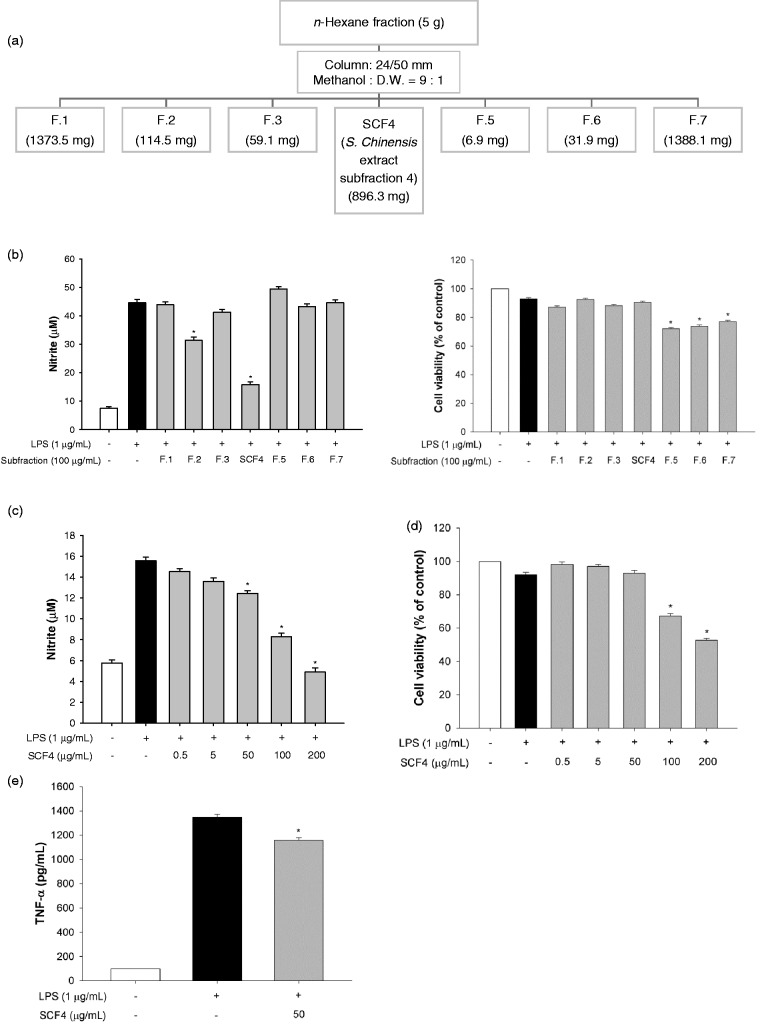
Figure 3.
SCF4 had a key role in the anti-inflammatory activity of the n-hexane layer of the SCE among the seven subfractions. (a) Schematic of the subfractionation of the n-hexane layer of the SCE. (b) Determination of the anti-inflammatory effect of the subfractions by estimation of nitrite production and cell viability after incubation with the fractions for 2 h. (c) Decreased nitrite production by SCF4 at concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 200 μg/mL. (d) SCF4 was not cytotoxic at concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 50 μg/mL. (e) SCF4 reduced LPS-activated TNF-α levels in cells. Data are the means ± SEM (n = 3), *p < 0.05. LPS: lipopolysaccharide; SCF4: subfraction 4 of the n-hexane layer of the EtOH extract of the aerial parts of S. chinensis; SCE: S. chinensis extract; SEM: standard error of the mean; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; DW: distilled water