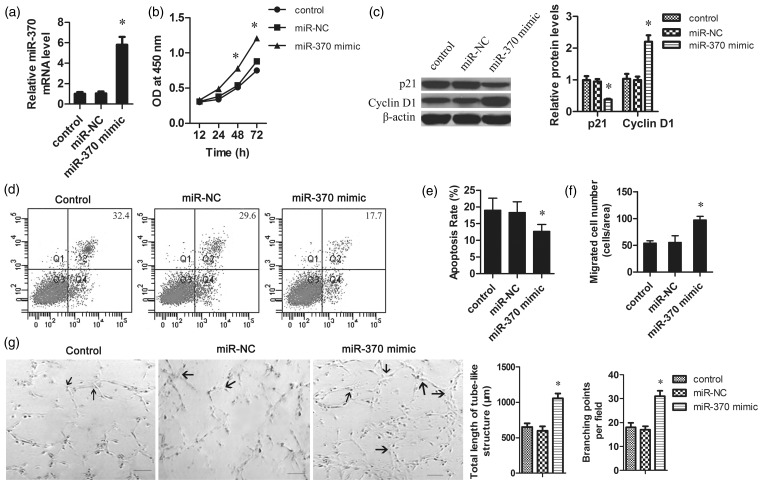
Figure 2.
The effect of miR-370 on the proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and angiogenesis of HUVECs. HUVECs were seeded at 1 × 105 cells per well in a 96-well plate. The miR-370 mimic or negative control was transfected into the HUVECs using Lipofectamine 2000. (a) Four hours post transfection, the mRNA levels of miR-370 in HUVECs were determined by qRT-PCR. The data were normalized according to β-actin. (b) MTT assays revealed that the overexpression of miR-370 promoted the growth of HUVECs. (c) Total protein was isolated from HUVECs with different treatments. The protein levels of p21 and cyclin D1 were measured by Western blot. β-Actin was used as the loading control. (d) Representative pictures of cells apoptosis determined by flow cytometry. Apoptosis of serum-starved HUVECs was analyzed by annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate and PI staining. (e) Quantification of apoptotic cells. (f) The migration ability of HUVECs was tested in a Transwell Boyden Chamber. (g) Representative pictures of Matrigel assays after overexpression of miR-370 in HUVECs. Endothelial network formation on Matrigel was quantified at 48 h from cell seeding. Angiogenesis was evaluated using Matrigel assays in vitro. The total length of tube-like structures and the number of branching points were quantified. Arrows indicated the capillary branch points. Scale bar 50 µm. *P < 0.05 vs. control group