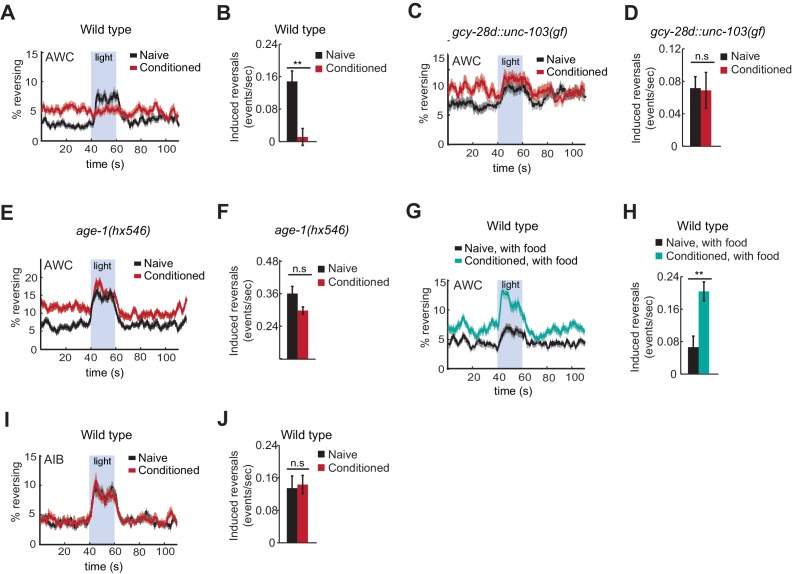
Figure 6. Behavioral responses to acute neuronal activation after odor conditioning.
(A,B) Light-induced reversals in naive or conditioned wild-type animals expressing Channelrhodopsin (ChR2) in AWCON. Data show the average fraction of animals executing reversals over time (A), or the difference between the number of reversals initiated during and after stimulation (20 sec each, B). (C,D) Light-induced reversals in naive or conditioned gcy-28d::unc-103(gf) animals expressing AWCON::ChR2. Note increased basal frequency of reversals, a known property of AIA inactivation (Chalasani et al., 2010). (E,F) Light-induced reversals in naive or conditioned age-1(hx546) animals expressing AWCON::ChR2. (G,H) Light-induced reversals in wild-type AWCON::ChR2 animals after appetitive conditioning. (I,J) Light-induced reversals in AIB::ChR2 animals after aversive conditioning. Pale blue regions in (A,C,E,G,I) represent blue light stimulation. Shaded regions and error bars represents S.E.M. n = 7–14 assays per condition, 18–25 animals stimulated five times per assay. P values were generated by t-test with correction for unequal variance (**p<0.001, n.s. not significant).
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.14000.015