Figure 3. Generation of a vps8 null mutant.
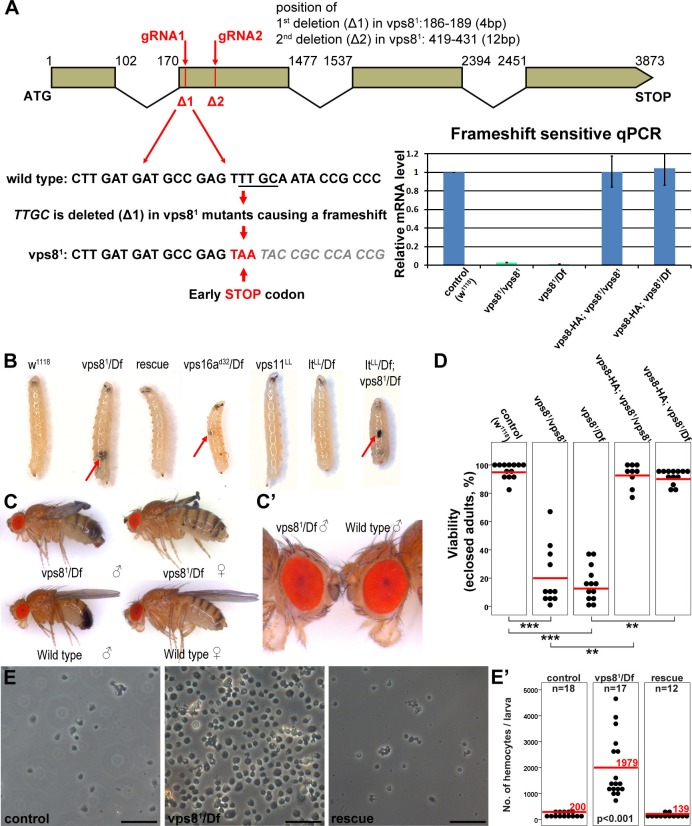
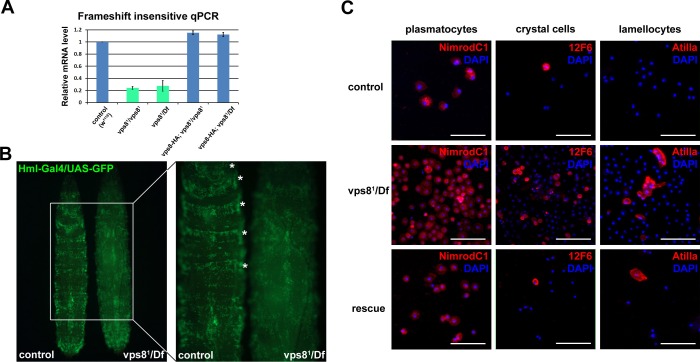
(A) Map of the vps8/cg10144 locus. CRISPR/Cas9-induced deletions in vps81 mutants are indicated with red lines. The sequence of the region containing the first microdeletion and the resulting early stop codon is indicated. The chart shows the results of qPCR analyses from animals of the indicated genotypes. Frameshift-sensitive primers were used to reveal that the amount of wild type vps8 transcript in mutants is negligible. The vps8 mRNA level is restored in mutants carrying the vps8-HA rescue transgene. (B) Photographs of larvae carrying mutations in various CORVET or HOPS subunit genes. Mutants of vps8, vps16a and double mutants lacking both vps8 and lt develop melanotic tumors (red arrows) in their body cavity. (C,C’) Photographs of adult vps81 mutant and control flies. Except for the wing spreading defects, the overall body structure of mutants is similar to wild type (C), including compound eye structure and pigmentation (shown enlarged in C’). (D) Dot plots show the percentage of adults that manage to eclose from the pupal case in the indicated genotypes. Each data point represents one experiment. The average number of eclosing mutant adults is decreased to 20% (vps81/vps81) and 16% (vps81/Df), and viability is restored by the vps8-HA transgene. Red lines represent the mean, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (E) Images of isolated hemocytes demonstrate that circulating hemocyte number is 10-fold higher in vps8 mutants than in controls or mutants expressing the Vps8-HA rescue transgene. (E’) shows the quantification of hemocyte data, with red lines and numbers representing mean hemocyte numbers. Bars: 50 µm in (E).