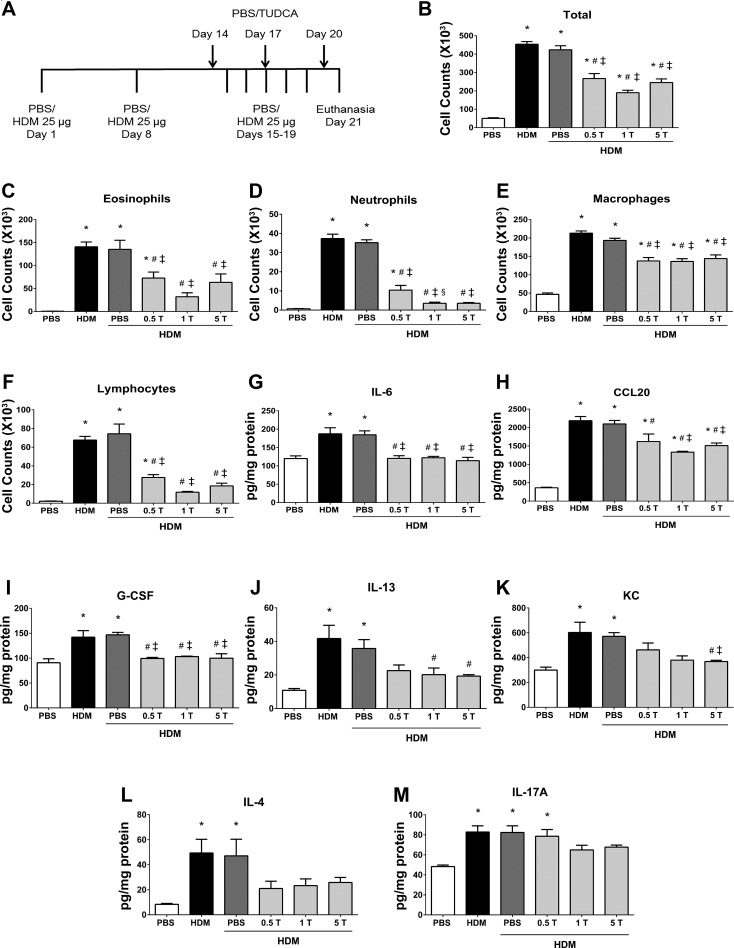
Fig. 1.
Preventive regimen of tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) attenuates house dust mite (HDM)-induced airway inflammation. A: schematic representing the time points of HDM or PBS instillation and TUDCA treatment. HDM (25 μg/mouse) was instilled intranasally while TUDCA (0.5, 1, and 5 mg/kg body wt) was administered via nasopharynx during the HDM challenge phase. B–F: analysis of inflammatory and immune cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Data are means ± SE of 6–8 mice/group. *P < 0.05 compared with their respective PBS controls. #P < 0.05 compared with vehicle-untreated HDM-challenged mice. ‡P < 0.05 compared with vehicle-treated HDM-challenged mice. §P < 0.05 compared with mice treated with 0.5 mg/kg TUDCA. G–M: analysis of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in lung lysates. Data are means ± SE of 6–8 mice/group. *P < 0.05 compared with their respective PBS controls. #P < 0.05 compared with vehicle-untreated HDM-challenged mice. ‡P < 0.05 compared with vehicle-treated HDM-challenged mice.