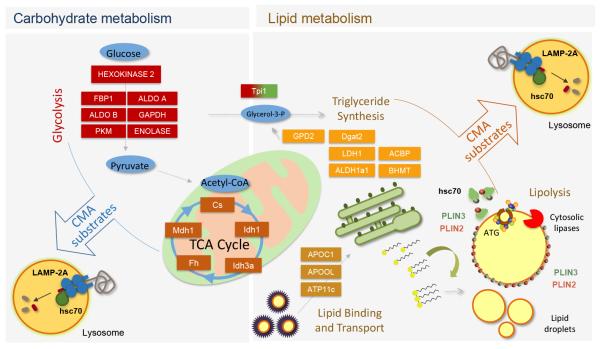
Figure 2. Contribution of CMA to regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism.
Left: CMA participates in the regulation of glycolysis by controlling levels of glycolytic enzymes and enzymes involved in the TCA cycle. Right: CMA modulates rates of lipid uptake and lipogenesis through the degradation of proteins involved in lipid binding and transport and enzymes of the triglyceride synthesis pathway. In addition, CMA determines rates of lipolysis through the selective removal of perilipins (PLIN), proteins that cover the surface of lipid droplets. Removal of perilipins is a pre-requisite to allow access to lipid droplets of cytosolic lipases and autophagy-related proteins (ATG) that initiate lipophagy.