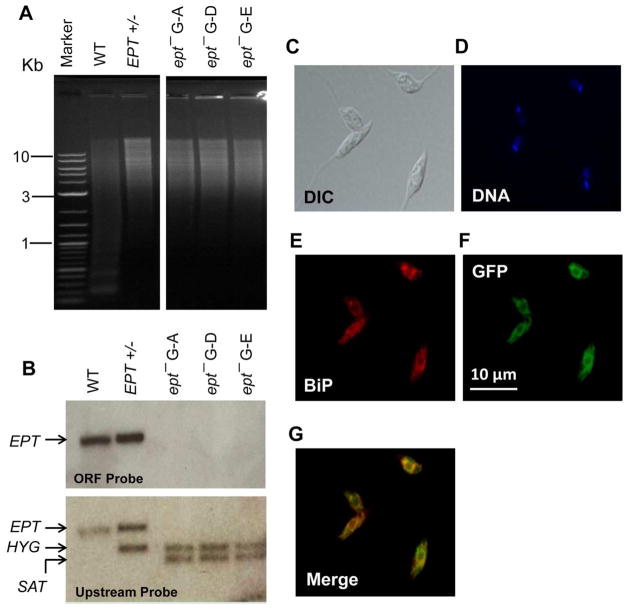
Figure 1. Targeted deletion and cellular localization of EPT in L. major.
(A) Genomic DNA samples (5 μg each) were digested with NcoI and XbaI, separated on a 0.8% agarose gel, and stained with ethidium bromide. (B) Southern blot was then performed using probes recognizing either the ORF (top) or an upstream region (bottom) of EPT. Replacement of EPT by HYG and SAT resistance genes was indicated in B. In A–B, WT: L. major LV39 wild type, EPT +/−: EPT heterologous mutant, ept− G-A, G-D, and G-E: three independent clones of EPT homozygous mutants. (C–G) Log phase promastigotes of ept−/+EPT-GFP were labeled with an ER marker (rabbit anti-T. brucei BiP antiserum followed by goat anti-rabbit IgG-Texas Red) and subjected to immunofluorescence microscopy. (C) Differential interference contrast (DIC) images; (D) Hoechst staining of DNA; (E) Anti-BiP staining; (F) GFP fluorescence; (G) Merge of E and F.