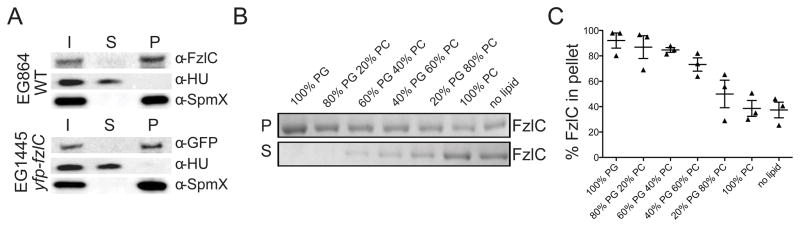
Figure 2. FzlC binds to membranes in vivo and in vitro.
(A) WT (EG864) or cells expressing yfp-fzlC as the only copy of fzlC (EG1445) were lysed and centrifuged to separate soluble (supernatant) and membrane (pellet) protein fractions. Whole cell lysate/input (I), soluble (S), and membrane (P) fractions were probed by immunoblotting for FzlC, as well as for SpmX (transmembrane protein) and HU (DNA-binding protein) as controls for membrane and soluble fractions, respectively. (B) Coomassie stained gels of supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions after copelleting of FzlC with sucrose loaded unilamellar vesicles with the indicated molar percentages of phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and phosphatidylcholine (PC). Abundance of FzlC in the pellet indicates degree of binding to vesicles. (C) Quantification of FzlC lipid binding shown in (B). % FzlC in pellet was calculated by dividing the FzlC pellet band intensity by the total FzlC band intensity (pellet and supe) for each reaction. Error bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) from three experimental replicates.