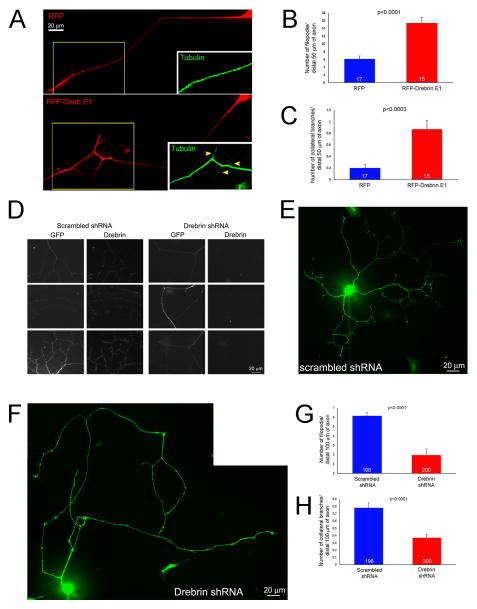
Figure 3.
Effects of drebrin E1 overexpression and shRNA-mediated depletion on axonal morphology. (A) Examples of the axons of cultured sensory neurons expressing RFP (control) or RFP-drebrin E1 at 24 hrs post-transfection. Drebrin expressing axons exhibited more filopodia and branches. The insets show tubulin staining for the boxed in regions. The RFP-drebrin branches contain tubulin staining, as expected for mature branches. (B) Quantification of the number of filopodia along the distal axons of RFP or RFP-drebrin E1 expressing neurons. Welch t-test. In all quantitative panels the sample sizes, axons, are denoted in the bars. (C) Quantification of the number of branches along the distal axons of RFP or RFP-drebrin E1 expressing neurons. Mann-Whitney test, medians of 0 and 1 respectively. (D) Examples of the efficacy of shRNA-mediated depletion of endogenous drebrin as detected by immunocytochemistry. Neurons expressing scrambled control shRNA contain detectable levels of drebrin along their axons. In contrast, by 3 days post transfection the axons of neurons expressing drebrin shRNA contain barely detectable drebrin, using identical imaging parameters. (E and F) Examples of the whole cell morphology of neurons cultured for 3 days following transfection with vectors expressing scrambled shRNA (E) and drebrin shRNA (F), the GFP-reporter signal is shown. (G) Quantification of the number of filopodia along distal axons in scrambled and drebrin shRNA expressing neurons. Welch t-test. (H) Quantification of the number of branches along distal axons in scrambled and drebrin shRNA expressing neurons. Mann-Whitney test, medians of 1 and 0 respectively.