FIGURE 3.
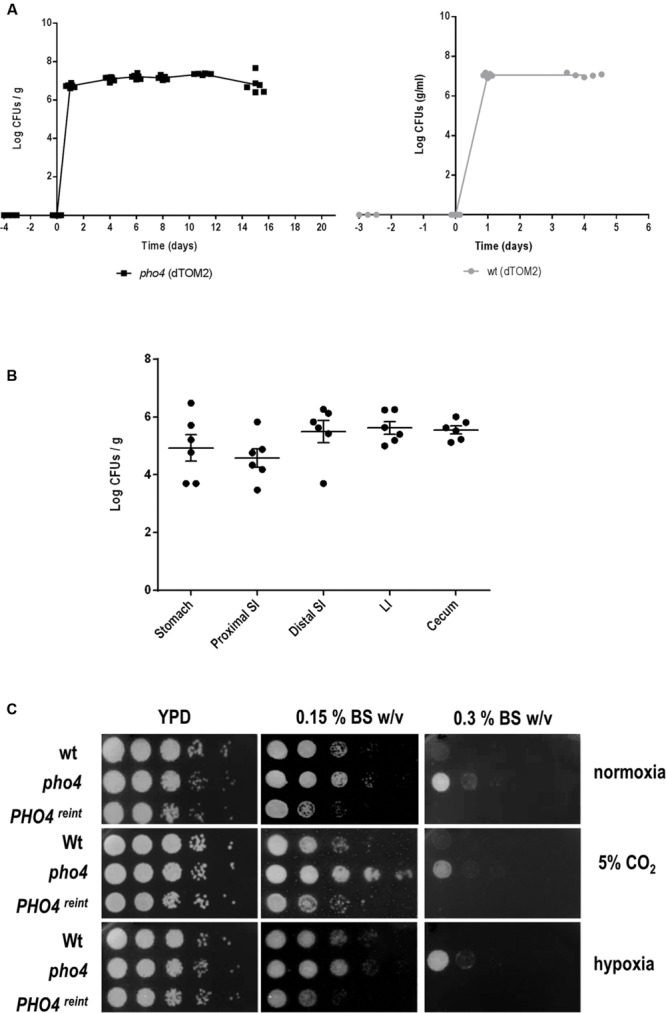
Role of Pho4 in murine gut colonization. (A) The pho4 mutant (left graph) and the wild type (right graph) strains tagged with the dTOM2 reporter gene were inoculated by gavage in antibiotic treated C57BL/6 mice. C. albicans colonization was followed in time by counting CFUs from stools. Graph represents Log CFUs/g of stools versus time. Each square represent a single mouse (n = 6). (B) Intestine from mice colonized with pho4-dTOM2 mutant were split on stomach, proximal small intestine (SI), distal small intestine, large intestine (LI) and cecum. Samples were processed and C. albicans colonies counted. Each single independent value is represented and the mean ± SEM from six mice. (C) Drop test was performed on YPD plates supplemented with Bile Salts (BS) to analyze the indicated strains susceptibility. Plates were incubated under the specified conditions at 37°C for 24 h (normoxia and 5% supplemented CO2 atmosphere) or 48 h (for plates incubated under hypoxia).
