Figure 1. The main filtering strategy for the variants identified in the exome sequencing.
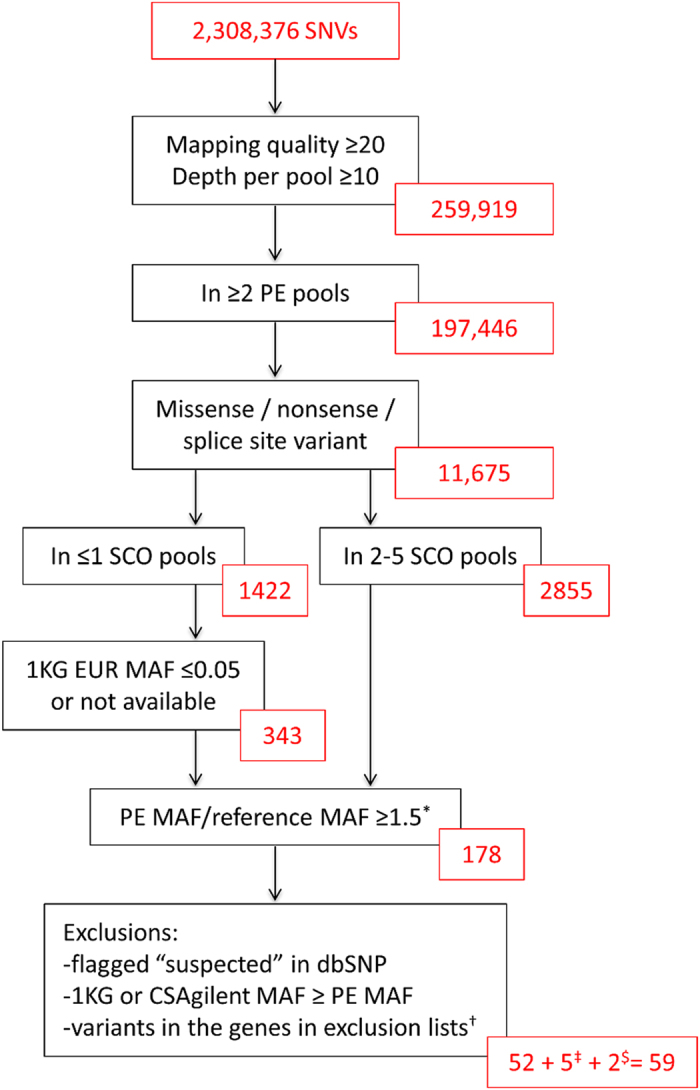
The variants that passed quality criteria and were found in at least two pre-eclampsia pools were filtered for function. To further narrow down the number of variants, pooled exome sequencing data from Swedish scoliosis patients as well as the 1000 Genomes European data and the Finnish Sequencing Initiative Suomi (SISu) data were utilised in the filtering. Variants remaining after each filtering step are indicated in red boxes. Based on the main filtering steps, 52 variants were selected. Furthermore, seven variants were selected based on additional filtering strategies. *The reference data used: the pooled exome sequencing data from Swedish scoliosis patients; the 1000 Genomes European data (APR 2012); and the Finnish SISU data (2014). †Fuentes Fajardo et al.34 and Ju et al.35. ‡The missense, nonsense and splice site variants with the 1000 Genomes European reference allele frequency ≤0.05, pre-eclampsia_refAllele/SISu and pre-eclampsia_refAllele/scoliosis_refAllele ≥1.5, reference allele present in ≤2 scoliosis pools and in over two pre-eclampsia pools. $A nonsense variant present in only one pre-eclampsia pool and a variant located in the previously identified linkage peak region were selected outside the main filtering strategy. 1 KG = The 1000 Genomes Project; MAF = minor allele frequency; PE = pre-eclampsia, SCO = the pooled exome sequencing data from Swedish scoliosis patients.
