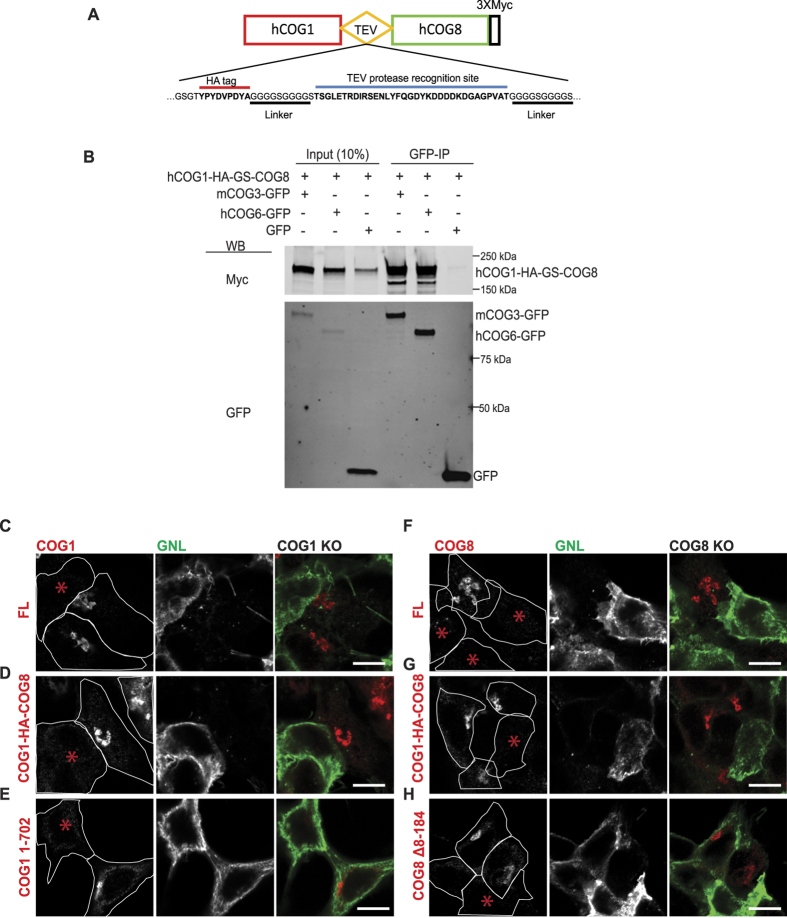
Figure 7. COG1-COG8 hybrid is incorporated into COG complex and properly localized to Golgi membranes.
(A) Schematic of the COG1-HA-GS-COG8 hybrid construct with flexible linker and TEV protease recognition site. (B) HEK 293 T cells were co-transfected with COG1-HA-GS-COG8 hybrid and either mCOG3-GFP, hCOG6-GFP, or GFP as a negative control. Cell lysates prepared 24 h after transfections were incubated with GBP-beads. IPs, along with 10% of total input, were separated on an SDS–PAGE gel, and blotted with anti-Myc (upper panel) and anti-GFP (lower panel) antibodies. ΔCOG1 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding either COG1-3Myc (C), COG1-HA-GS-COG8 hybrid (D) or COG1 1-702-3Myc (E). ΔCOG8 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding either COG8-3Myc (F), COG1-HA-GS-COG8 hybrid (G), or COG8 Δ8-184-3Myc (H). 72 hours after transfection cells were fixed and surface labeled with GNL-647 and stained with anti-Myc antibodies for confocal microscopy analysis. Cell outlines overlaid with the Myc channel. COG1-HA-GS-COG8 hybrid is capable of rescuing the glycosylation defect in both ΔCOG1 and ΔCOG8 cells. COG1 or COG8 lacking the interaction site for their respective partner will not rescue the COG subunit KO glycosylation defect phenotype. Size bar, 10 μm. * Denotes a non-transfected/un-rescued KO cell.