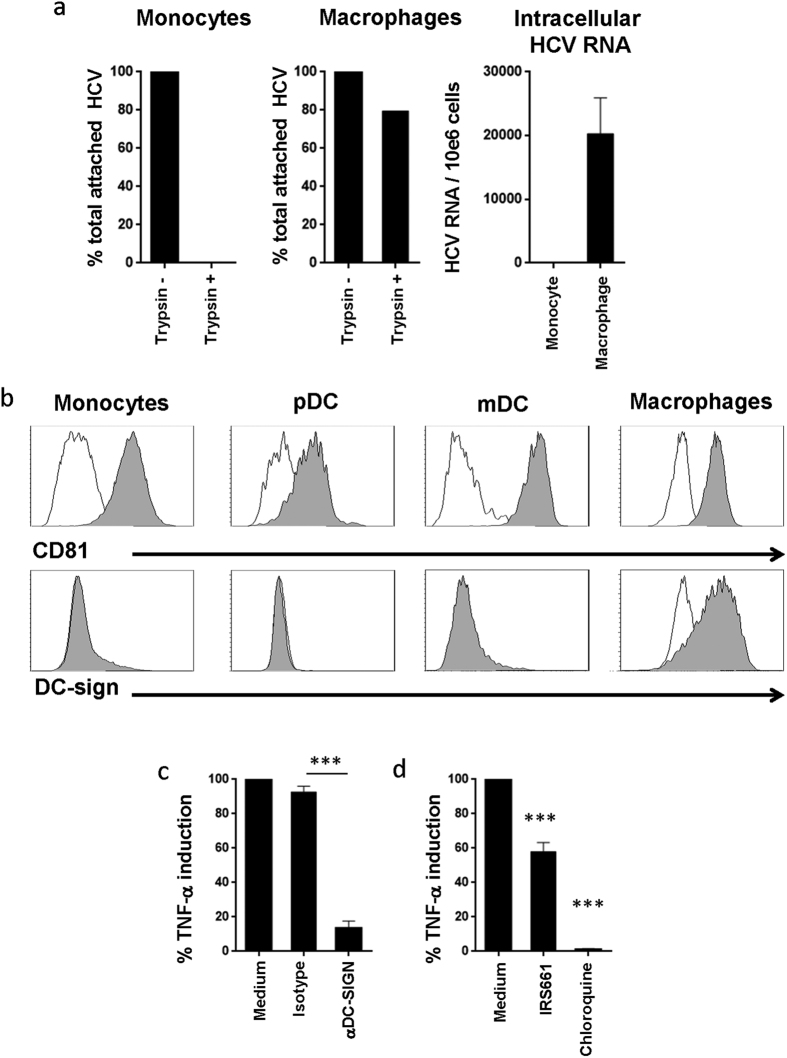
Figure 6. DC-SIGN and TLR7/8 are important for the uptake and recognition of HCV particles by macrophages.
(a) Macrophages and monocytes (105/200 μl) were incubated with HCV particles at 37 °C for 4 h, and then cells were washed and treated with trypsin at 37 °C for 5 mins to remove cell surface-attached viral particles. After extensive wash, total RNA was extracted and viral RNA was measured by real-time PCR. Viral RNA copies were normalized to GAPDH. Results were generated with cells from 3 different donors and represent the percentage of viral RNA associated to the cells untreated with trypsin. (b) PBMCs or Macrophages were stained with isotype control (open histograms), anti-CD81 or anti-DC-SIGN Abs (filled histograms). CD81 and DC-SIGN expression were measured on monocytes (CD14+), mDCs (Lin−CD14−HLA-DR+CD11c+CD123−/dim) and pDCs (Lin−CD14−HLA-DR+CD11c−CD123+) by flow cytometry using cells from 3 different donors. Macrophages were also stained with anti-CD81-PE or anti-DC-SIGN-PE Abs. (c) Macrophages were incubated with medium alone, isotype control Abs, or DC-SIGN blocking Abs (10 μg/ml) for 1 h, then cells were exposed to HCV particles for 24 h. Levels of TNF-α in cell culture supernatants were quantified by ELISA. Shown are percentages of TNF-α production relative to cells exposed to HCV particles alone. Results were generated with cells from 6 different donors. Two tail paired student’s t-T tests analysis-values are indicated on the graphs. (d) Macrophages were stimulated with HCV particles in the presence or absence of the TLR7/8 inhibitor IRS661 (10 μg/ml) or chloroquine (10 μM) for 24 h. TNF-α production was measured by ELISA. Results represent mean ± SD values generated with cells from 5 different individuals. Dunnett’s test p-values are indicated on the graphs (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001).