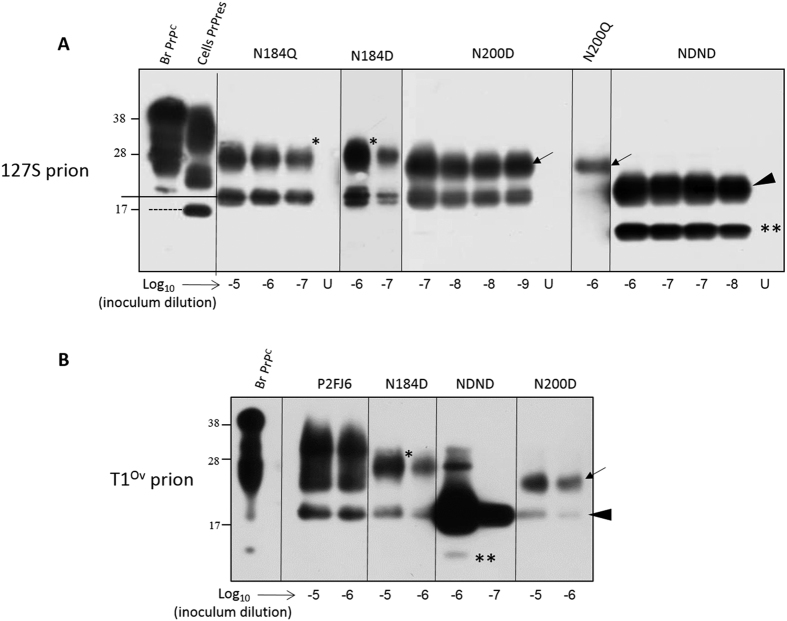
Figure 5. Efficient conversion of PrPC glycosylation mutants by two distinct prions in Cell-mb-PMCA reactions.
Lysates from RK13 cells expressing ovine PrPC mutated on the first N-glycosylation site at residue 184 (N184Q, N184D), on the second glycosylation site at residue 200 (N200D, N200Q) or at both residue (NDND) glycosylation sites were mixed with PrP0/0 brain lysate (1:1 dilution), seeded with serial 10-fold dilutions of tg338 brain homogenate containing either 127S (A) or T1Ov (B) prions and submitted to 2 rounds of Cell-mb-PMCA. Lanes U contains unseeded controls. All samples were PK-treated before western blot analysis (Sha31 antibody). For comparison, the electrophoretic profiles of tg338 brain PrPC (lane Br. PrPC) and P2FJ6 PrPres (lane Cell PrPres) are shown. To facilitate the interpretation of the western blot, PrPres monoglycosylated at residue 200 or 184 are indicated by asterisks and arrows, respectively. Full-length unglycosylated PrPres is indicated by an arrowhead. **Indicates low size PrPres fragments, highly abundant following conversion of unglycosylated PrPC by 127S but not by T1Ov prions.