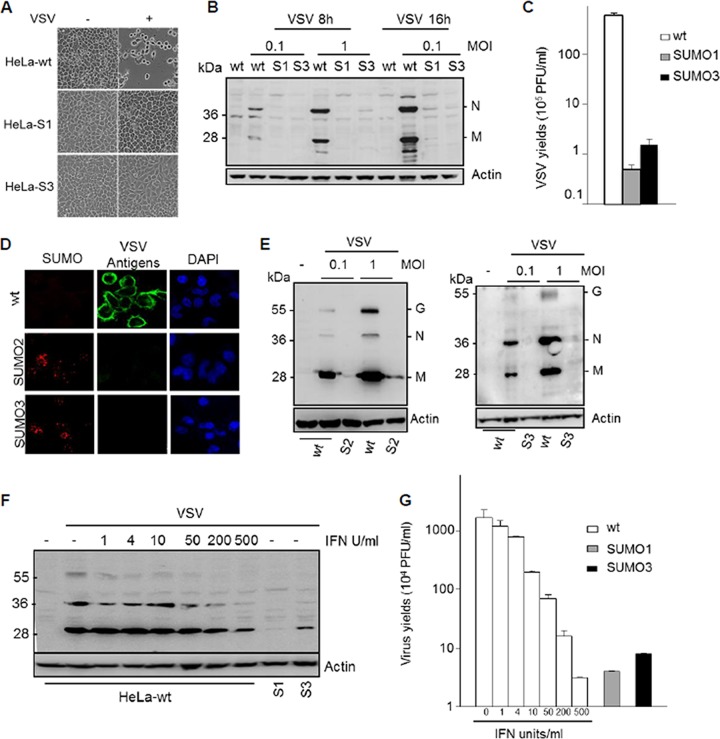
FIG 1.
SUMO confers resistance to VSV. (A) SUMO1 and SUMO3 protected cells from VSV-induced cell lysis. HeLa-wt, HeLa-SUMO1 (HeLa-S1), and HeLa-SUMO3 (HeLa-S3) cells were not infected (−) or infected (+) with VSV at an MOI of 0.1 for 16 h. The phase-contrast picture was acquired using a Nikon Eclipse TS100 microscope and Coolpix lens camera. Magnifications, ×10. (B) HeLa-wt, HeLa-SUMO1 (S1), and HeLa-SUMO3 (S3) cells were infected with VSV for 8 h or 16 h. Equal amounts of cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting for the expression of VSV antigens and actin. (C) The supernatants of cells infected at an MOI of 0.1 for 16 h were used for the determination of virus yields. Mean values and standard deviations from three independent experiments are shown. (D) U373MG-wt, U373MG-SUMO2, and U373MG-SUMO3 cells were infected for 8 h at an MOI of 0.1 or 1. Double immunofluorescence was performed with cells infected at an MOI of 1 with anti-SUMO2/3 (red) and anti-VSV (green) antibodies. The nucleus was stained with DAPI. (E) Extracts from cells infected at different MOIs were analyzed by Western blotting for the expression of VSV antigens and actin. S2, U373MG-SUMO2 cells; S3, U373MG-SUMO3 cells. (F, G) Comparative effects of IFN and SUMO on VSV inhibition. HeLa-wt cells were treated for 24 h with 1, 4, 10, 50, 200, and 500 units/ml of IFN-α. Then, IFN-α-treated HeLa-wt, HeLa-SUMO1, and HeLa-SUMO3 cells were infected with VSV at an MOI of 1 for 8 h. (F) Extracts of infected cells were analyzed by Western blotting for VSV proteins and actin. (G) The supernatants were used to determine the virus yields. Mean values and standard deviations from three independent experiments are shown.