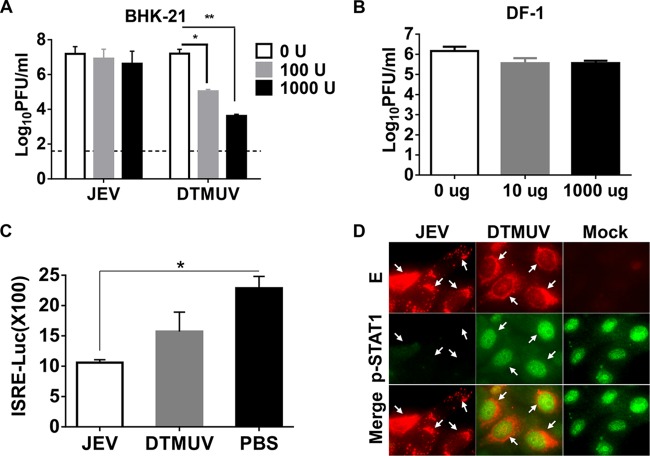
FIG 4.
DTMUV is sensitive to the type I IFN response in mammalian cells. (A) Antiviral effects of IFN-α in mammalian cells. BHK-21 cells were treated with medium containing various doses of IFN-αA/D (0, 100, or 1,000 U) and then infected with DTMUV or JEV at an MOI of 1. The supernatants were collected, and the viral titers were determined by plaque assay in BHK-21 cells at 24 h postinfection. Statistically significant differences are indicated. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (B) Antiviral effects of IFN-α in avian cells. DF-1 cells treated with the indicated concentrations of avian IFN-αA/D were subjected to DTMUV infection, and viral titers were then determined by plaque assay at 24 h postinfection. (C) ISRE reporter assays. BHK-21 cells were transfected with the corresponding reporter plasmids and then infected with DTMUV or JEV in the presence of 100 U IFN-αA/D. A luciferase assay was performed using a dual-luciferase assay kit, and the results were calculated accordingly. Statistically significant difference is indicated. *, P < 0.05. (D) Nuclear translocation assay of p-STAT1. Vero cells infected with DTMUV or JEV were then subjected to IFN-αA/D (1,000 U/ml) treatment. The cells were fixed and immunostained by using rabbit anti-p-STAT1 (green) and mouse antiserum specific for DTMUV or JEV (red). Arrows, examples of viral proteins and/or nuclear staining of p-STAT1.