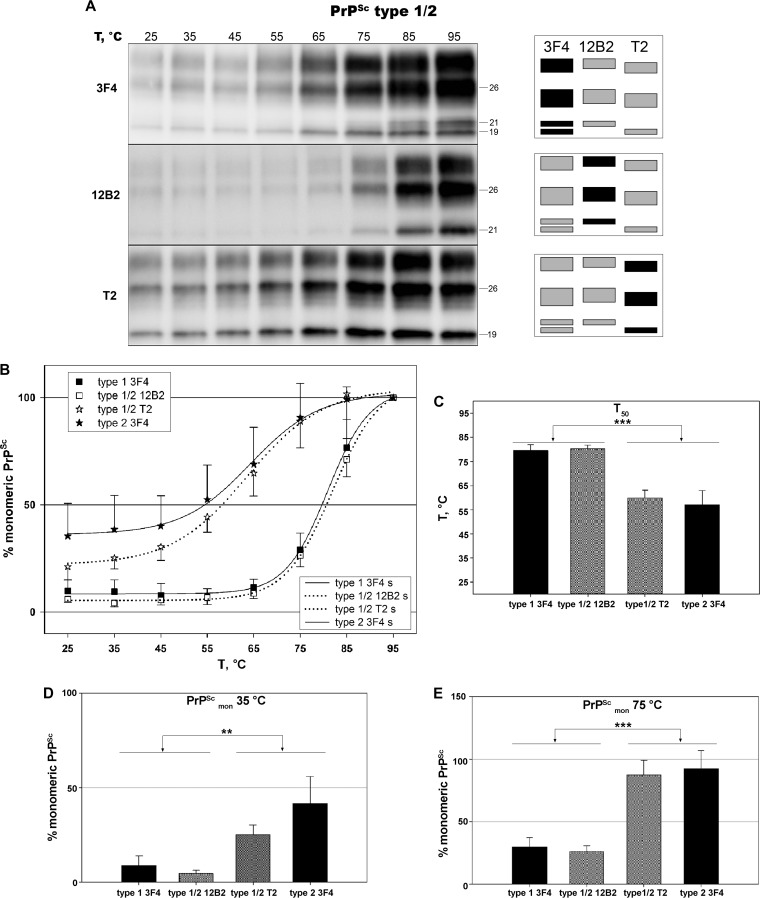
FIG 6.
In vivo cooccurring MM1 and MM 2C prions maintain the distinctive thermostability of the corresponding pure CJD type. PK-digested brain samples were subjected to increasing temperatures, followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. (A) Representative immunoblots of TSA performed on an MM1 + 2C sample, probed with primary antibodies 3F4, 12B2, and T2. (B) Plots of temperature solubility assay data sets for PrPSc types 1 and 2, when cooccurring prions (MM1 + 2C) are compared to those of the corresponding pure type (MM1 and MM 2C, respectively). Type-specific antibodies 12B2 and T2 have been used to obtain accurate separate measurements of type 1 and type 2 signals in mixed samples. Symbols represent data, expressed as means ± standard deviations, and lines represent the sigmoid curves (s) that best fit the data. (C) Comparison of T50 values between pure and mixed variants. The triple asterisk (***) indicates a statistically significant difference between groups at P values of <0.001. (D) Comparison of the percentage of monomeric PrPSc at 35°C between pure and mixed variants. The double asterisk (**) indicates a P value of <0.05 between groups with the exception of type 1 3F4 versus type 1/2 T2 (not significant). (E) Comparison of the percentages of monomeric PrPSc at 75°C between pure and mixed variants. The triple asterisk (***) indicates a P value of <0.001 between groups.