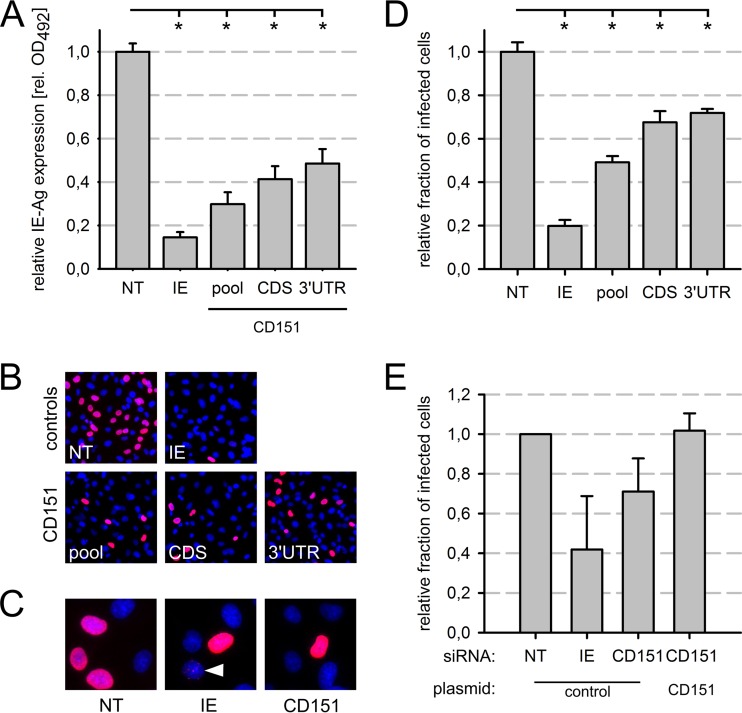
FIG 3.
CD151 siRNAs specifically reduced the infection of EA.hy926 cells. (A to D) Individual CD151 siRNAs from the siRNA pool used in the screen or an equimolar mixture thereof were transfected 48 h prior to infection. Immediate early antigen (IE-Ag) expression was measured by ELISA (A), and the fraction of infected cells was determined by indirect immunofluorescence staining of IE-Ag (B and D) with a primary antibody and a Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody (red). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (C) Magnified images showing pan-nuclear (NT, IE, and CD151 siRNAs) or punctate (IE siRNA) (white arrowhead) expression pattern of IE-Ag. siRNAs: NT, nontargeting pool; IE, immediate early antigen; CDS, CD151 coding sequence; 3′ UTR, CD151 3′ untranslated region; pool, equimolar mix of both CD151 siRNAs. (E) A CD151 siRNA that targets the 3′ UTR of the CD151 gene was cotransfected with a plasmid encoding either GFP (as a control) or a CD151-GFP transgene resistant to the siRNA. NT siRNA was used as a reference, and IE siRNA was used as a positive control. The data were standardized to the negative control (NT siRNA plus GFP plasmid). The graph shows mean values for three independent experiments. Error bars show standard errors of the means. n.s., not significant; *, significant (P < 0.05; Student's t test).