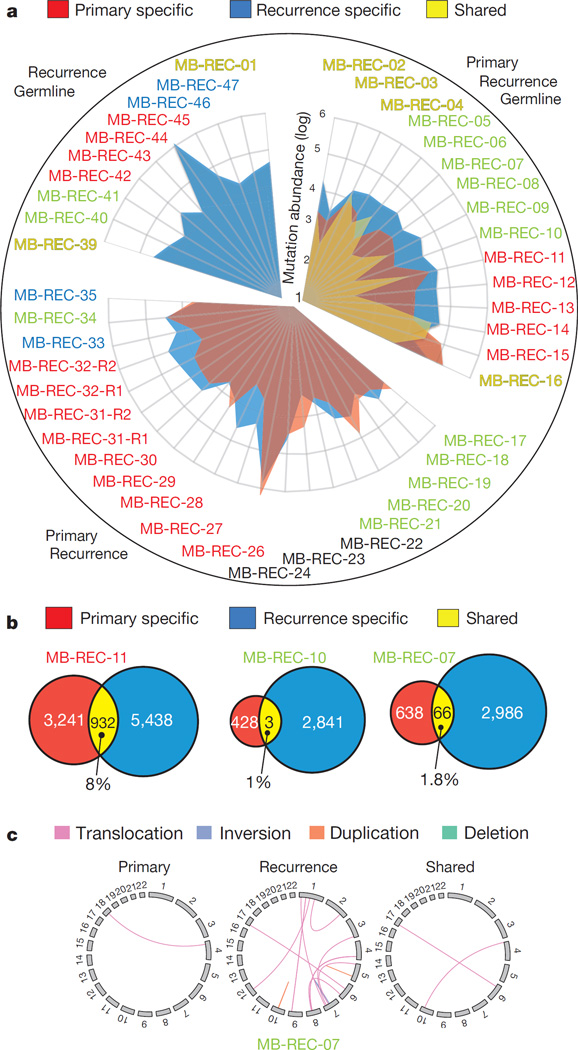
Figure 3. Major genetic divergence of human untreated medulloblastoma and patient-matched recurrences determined by whole-genome sequencing.
a, Somatic mutation burden in 45 tumours (43 patients) was increased fivefold in matched post-treatment (blue) versus therapy-naive (red) tumours (Student’s t-test; P value = 2.7 × 10−4). On average, 11.8% of mutations are shared somatic events (n = 15 cases with germline). Hypermutated samples stand out by two orders of magnitude (MB-REC-26/44). Patient subgroup is indicated by the label (blue, Wnt; red, Shh; yellow, Group 3; green, Group 4; black, undetermined). b, Venn diagrams of three representative patients reveal a minimal overlap in genetic events between therapy-naive (red) and recurrent (blue) tumours. c, Circos plot in a representative patient illustrates compartment-specific somatic structural variations.