FIG 10.
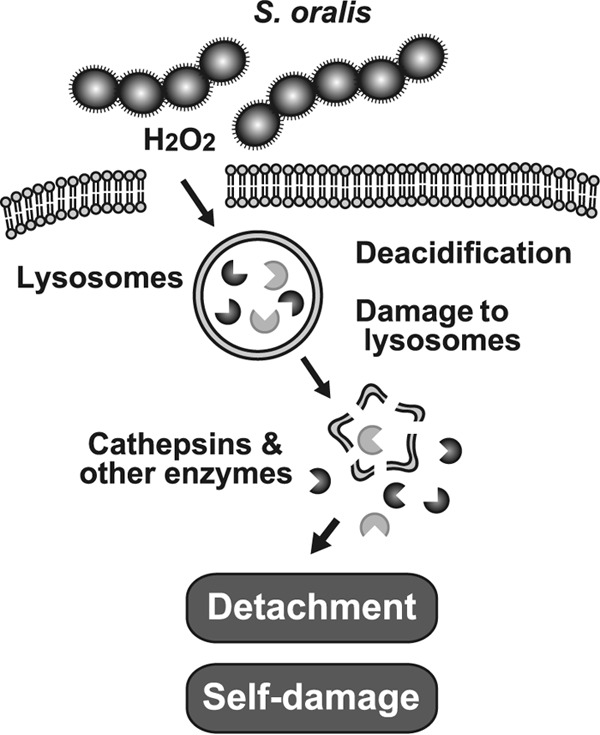
Proposed model illustrating the role of H2O2 in S. oralis-induced macrophage death. H2O2 causes lysosomal deacidification and the destruction of lysosomal integrity via Fenton's reaction, followed by leakage of cathepsins and other lysosomal hydrolytic enzymes. These cytotoxic enzymes degrade cellular components and induce self-damage in S. oralis-infected cells. Cathepsins are implicated in the detachment of the dead cells from the culture plates.
