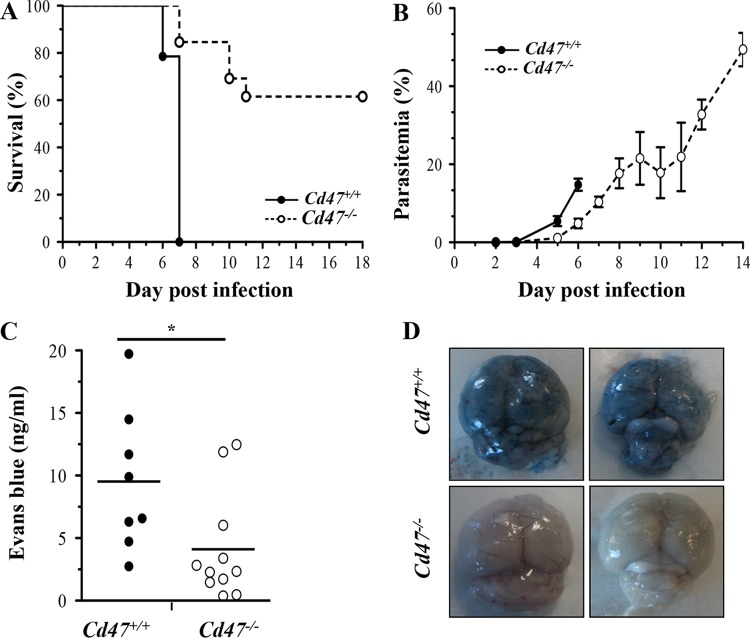
FIG 1.
Cd47−/− mice are less susceptible to P. berghei ANKA ECM. (A) Survival curves following challenge with 1 million P. berghei ANKA-infected erythrocytes by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection for Cd47+/+ mice (solid line) versus Cd47−/− mice (dashed line). P < 0.0001 by log-rank test; n = 13 mice/group. (B) Parasite burdens as assessed by peripheral parasitemia were significantly decreased in Cd47−/− versus Cd47+/+ P. berghei ANKA-infected mice but increased progressively. P < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA; P < 0.05 by Sidak's multiple test comparing Cd47+/+ versus Cd47−/− on day 5 and day 6; n = 10 mice/group. The parasitemia and survival curves are from one representative experiment out of the three performed. The error bars represent standard errors of the mean (SEM). (C and D) An Evans blue dye extravasation assay was performed on days 6 and 7 postinfection to assess microvascular leakage into the brain parenchyma. Shown are photographs of representative brains from P. berghei ANKA-infected Cd47+/+ mice (top) and Cd47−/− mice (bottom) (D) and quantification of Evans blue dye in the brains (C) (*, P = 0.0232; Mann-Whitney test; n = 8 for Cd47+/+ mice and n = 11 for Cd47−/− mice). The points represent individual animals, and the lines are group means.