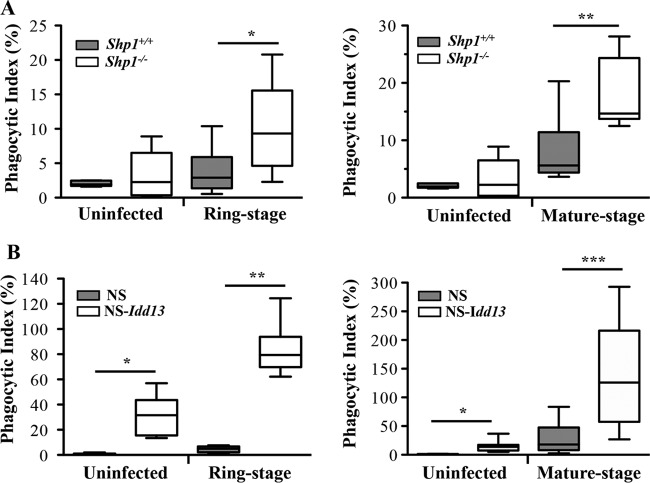
FIG 4.
Genetic disruption of CD47-SIRPα interactions increases phagocytosis of P. falciparum-infected RBCs by murine macrophages. Uninfected RBCs and P. falciparum-infected ring-stage (left) and mature-stage (right) RBCs were incubated with macrophages from mice with SHP1 deficiency (Shp1−/−) (A) and variant SIRPα mice (NS-Idd13) (white boxes) compared to their wild-type counterparts (gray boxes) (B). Differential uptake of parasitized RBCs at ring stage and mature stage by macrophages from wild-type mice versus Shp1−/− mice (A) (*, P = 0.022, and **, P < 0.0001; Mann-Whitney test) and macrophages from NS versus NS-Idd13 mice (B) (*, P = 0.005; **, P = 0.0022; ***, P = 0.0006; Mann-Whitney test) was observed. The results are the combined data from three experiments and are shown as box-and-whisker plots, representing interquartile and complete ranges, with the horizontal line in each box indicating the median level of phagocytic index.