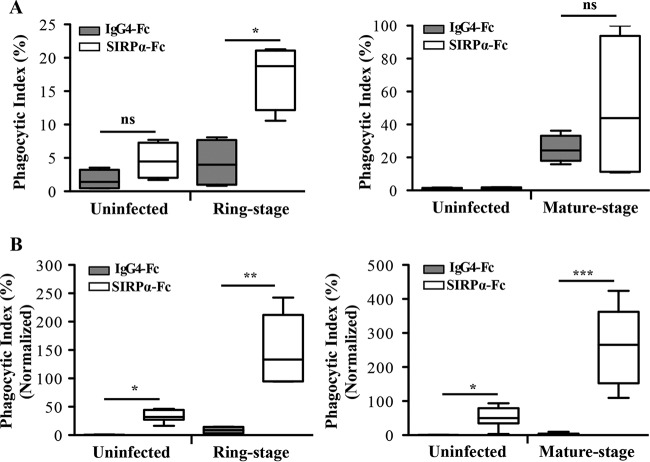
FIG 6.
Functional blockade of SIRPα signaling by human SIRPα-Fc in phagocytosis assays. LPS- and IFN-γ-prestimulated macrophages were incubated with uninfected or ring-stage- or mature-stage-P. falciparum-infected RBCs in the presence of SIRPα-Fc (white boxes) and the isotype IgG4-Fc control (gray boxes). (A) Human MDMs prestimulated with LPS and IFN-γ showed increased uptake of both ring-stage- and mature-stage-P. falciparum-infected RBCs. Comparisons of phagocytic indexes between control IgG4-Fc- versus SIRPα-Fc-treated macrophages with ring-stage-P. falciparum-infected RBCs are shown. *, P = 0.005; ns, not significant; n = 4; t test. The data are the combined results from two experiments. (B) Mouse SN macrophages showed a significant increase of both ring-stage and mature-stage parasites. The values of the phagocytic indexes were normalized to 100% infected RBCs as described previously (15) using the following calculation: I = (Tot − N × n)/(1 − n), where I is the concentration of CD47 on 100% infected RBCs, Tot is the anti-CD47 bound on uninfected RBCs and infected RBCs, N is the anti-CD47 bound on uninfected RBCs, and n is the fraction of uninfected RBCs. Comparisons for uninfected-RBC and infected-RBC uptake for ring-stage- and mature-stage-P. falciparum-infected RBCs are shown (*, P = 0.005; **, P = 0.0022; ***, P < 0.0001). The data were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney test and are the combined results of at least three experiments. The results are shown as box-and-whisker plots, representing interquartile and complete ranges, with the horizontal line in each box indicating the median level of phagocytic index.