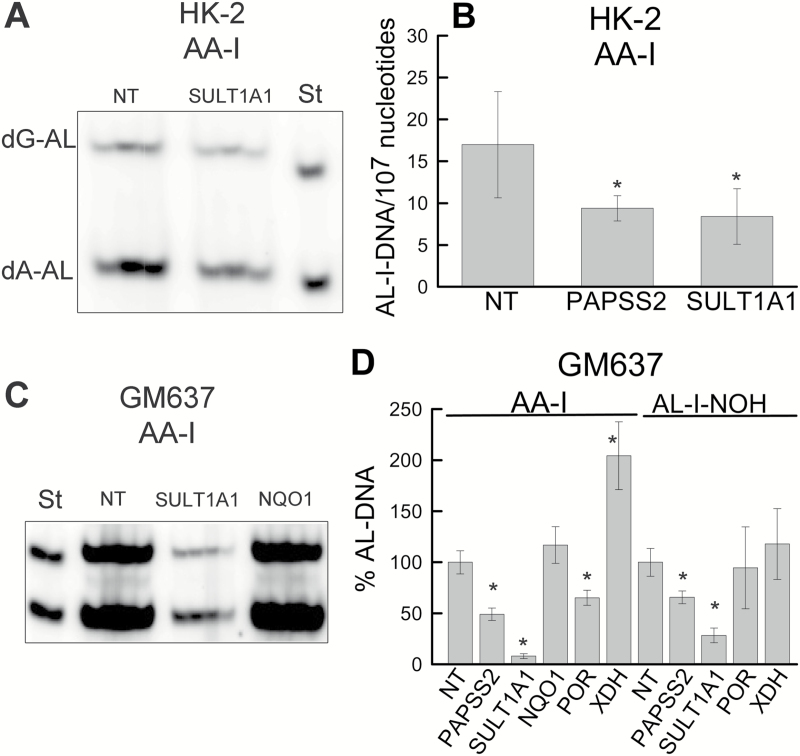
Figure 5.
Genotoxicities of AA-I and AL-I-NOH in cultured cells silenced for selected biotransformation genes of AA-I. At 30% cell density, HK-2 and GM637 cultures were treated with siRNAs for 2 and 3 days, respectively, before introducing 25 µM of one of the test compounds. Following exposure to the compound, 6h for HK-2 cells and 24h for GM637, DNA (5 µg) was subjected to adduct analysis. Panels (A) and (C) are representative fragments of two separate polyacrylamide gels showing the results of postlabeling analysis in HK-2 and GM637 cells, respectively, treated with NT, SULT1A1 or NQO1 (GM637 cells only) siRNA followed by AA-I exposure. St—mixture of standard oligonucleotides with dG-AL-II (upper band) and dA-AL-II adducts (lower band), 15fmol of each in (A) and 30fmol of each in (C). Each well represents a digestion mixture corresponding to one cell culture plate. The well between each siRNA exposure conditions and standards is left empty. Three and four digestion reactions are shown for HK-2 (A) and GM637 (C) gels, respectively. (B) AL-I-DNA adduct levels in HK-2 cells exposed to AA-I and various siRNAs. (D) AL-I-DNA levels in GM637 cells exposed to AA-I or AL-I-NOH, expressed as percentage from adduct levels data in cells treated with NT siRNA. Results are shown as the mean ± SD for at least two independent cell passages. As compared with the NT group, * indicates P < 0.05. In experiments with AA-I and AL-I-NOH, the levels of AL-I-DNA in GM637 cells treated with NT siRNA were 180±25 adducts/107 nucleotides and 235±41 adducts/107 nucleotides, respectively.