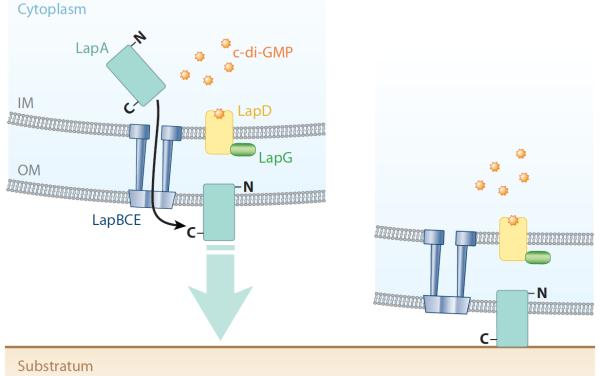
Figure 3.
c-di-GMP effector system in Pseudomonas fluorescens. This diagram depicts a summary of the current model for the c-di-GMP effector system in P. fluorescens, which impacts the motile-to-sessile transition. The LapA protein, a predicted cell-surface adhesion, is transported to the cell surface through the ABC transporter, comprised of the LapBCE proteins. LapD binds c-di-GMP, and through an inside-out signaling mechanism, the periplasmic domain of LapD binds LapG. Thus, LapG is prevented from cleaving and releasing LapA from the cell surface, thereby promoting biofilm formation (Newell et al. 2011a; Illustration courtesy of William Scavone, MA, CMI, Kestrel Illustration Studio, LLC). Abbreviations: GMP, guanosine monophosphate; IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane.