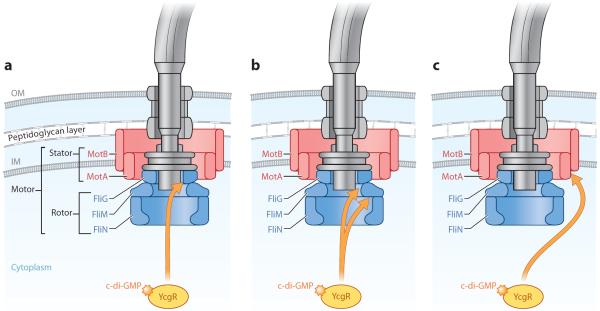
Figure 4.
c-di-GMP effector system in Escherichia coli. This diagram depicts a summary of the current models of the c-di-GMP effector system in E. coli, which impacts the motile-to-sessile transition. YcgR bound to c-di-GMP stimulates YcgR to interact with one or more components of the flagellar motor, reducing or altering motor function and thus promoting the motile-to-sessile transition. (a) Fang & Gomelsky (2010) suggest that c-di-GMP-bound YcgR interacts with FliG and disrupts the FliG-FliM interaction. An increased bias in counterclockwise flagellar rotation ensues, which leads to poor migration and thus facilitates the motile-to-sessile transition. (b) Paul et al. (2010) suggest that c-di-GMP-bound YcgR binds to FliM, disrupting the FliG-FliM interaction and thereby promoting a counterclockwise rotational bias. They also propose that YcgR also interacts with FliG, which leads to a disruption in the FliG-MotA interactions and a reduction in torque generation. (c) Boehm et al. (2010) suggest that c-di-GMP-bound YcgR interacts with MotA to reduce flagellar motor function. Illustration courtesy of William Scavone, MA, CMI, Kestrel Illustration Studio, LLC. Abbreviations: GMP, guanosine monophosphate; IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane.