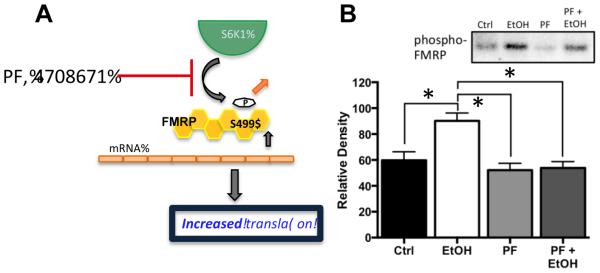
Figure 4.
Inhibition of S6K1 prevents chronic ethanol-induced increases in phospho-FMRP. (A) Schematic representation of the effect of the S6K1 inhibitor PF-470861 (PF) on phosphorylation of FMRP at S499. Reduced phosphorylation of FMRP results in reduced inhibitory binding of mRNA and an increase in the pool of mRNA transcripts available for translation. (B) Immunoblot analysis revealed that while treatment of organotypic hippocampal cultures with PF (6 μM) had no effect on the phosphorylation status of FMRP at S499 under control conditions, it completely blocked the chronic ethanol-induced increase in phospho-FMRP (n = 5). Data represent mean ± SEM, ** p < 0.01.