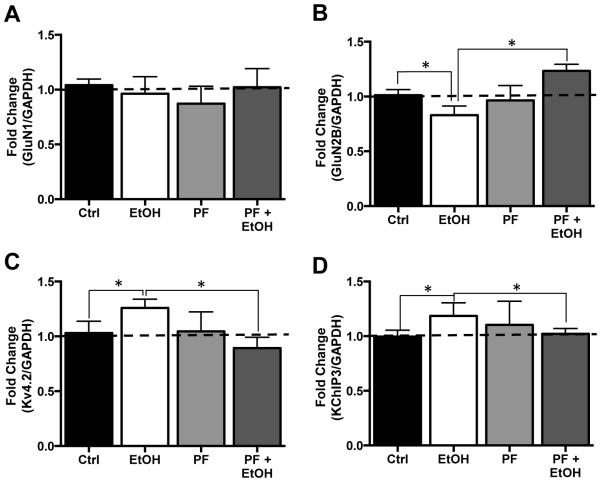
Figure 6.
Inhibition of S6K1 prevents ethanol-induced changes in binding of NMDA and Kv4.2 mRNA transcripts to FMRP. (A) In organotypic hippocampal slice cultures, neither ethanol, (75 mM), the S6K1 inhibitor PF-470861 (PF, 6 μM) alone or ethanol plus PF altered the binding of GluN1 mRNA to FMRP (n=6). (B) GluN2B mRNA binding to FMRP was reduced in response to chronic ethanol exposure alone while exposure to PK had no effect of GluN2B binding of FMRP. The effect of ethanol was blocked by the addition of PK, which resulted in a significant increase in GluN2B mRNA association with FMRP compared to control (Ctrl). In contrast, binding of mRNA coding for Kv4.2 (C) and KChIP3 (D) were significantly increased in cultures chronically exposed the ethanol. This increase was prevented by co-incubation with PK. Data represent mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05.