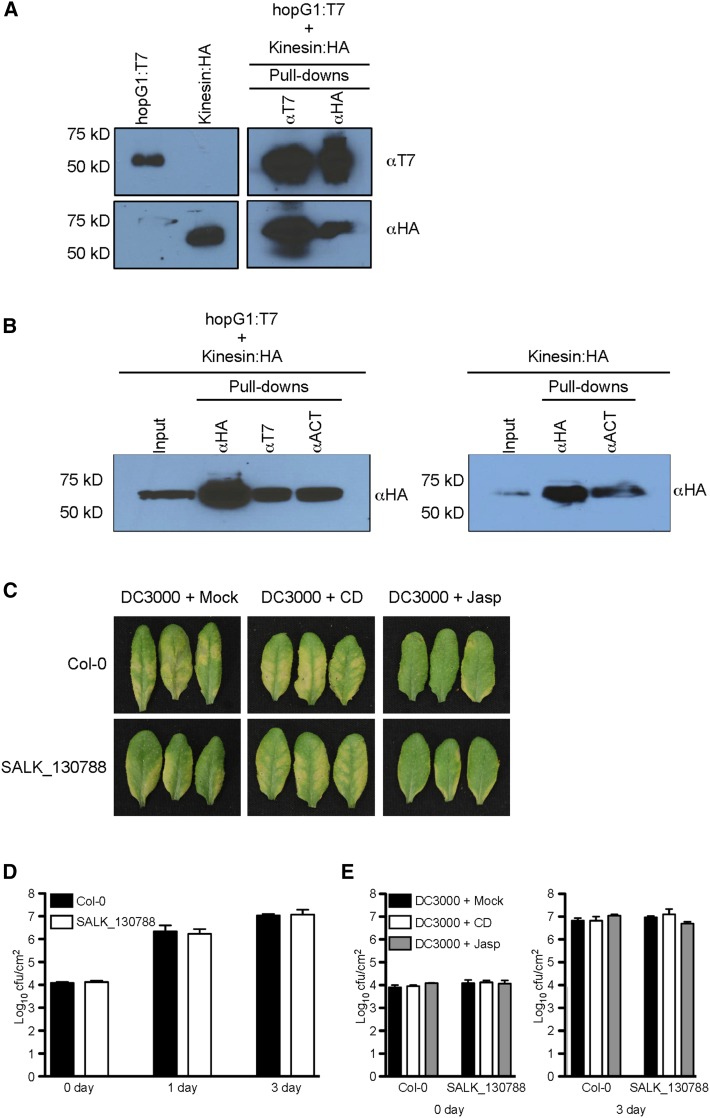
Figure 7.
HopG1 induces host disease symptoms through the function of a mitochondrial-localized kinesin. A, The Pst DC3000 T3E HopG1 interacts with the N-terminal half of an Arabidopsis kinesin (At4g39050). Epitope-tagged fusions to the open-reading frame of HopG1 (T7) and the first 978 nucleotides of kinesin (HA) were transiently expressed (40 h) in N. benthamiana and protein extracts were isolated and analyzed for a specific interaction between HopG1 and kinesin using co-immunoprecipitation assays. B, Kinesin and HopG1 are associated with the host actin cytoskeleton. Epitope-tagged fusions to the first 978 nucleotides of kinesin (HA) and the open-reading frame of HopG1 (T7) were transiently expressed (40 h) in N. benthamiana and total protein extracts were analyzed by co-immunoprecipitation analysis for a specific interaction among kinesin, HopG1, and the actin cytoskeleton (left blot), and an interaction between kinesin and the actin cytoskeleton (right blot). C, A mitochondrial-localized kinesin is required for Pst DC3000-induced symptom development. Five-week-old plants were co-infiltrated with either MgCl2, cytochalasin-d, or jasplakinolide and Pst DC3000 at a concentration of 2 × 105 cfu ml−1, and plants were monitored for the induction of chlorosis. Wild-type Col-0 plants inoculated with Pst DC3000 showed visible signs of disease at 3 dpi. When plants were co-inoculated with Pst DC3000 and cytochalasin-d, pathogen-induced chlorosis phenotype was enhanced; in the presence of jasplakinolide, the chlorosis phenotype was reduced. In the Arabidopsis kinesin mutant, inoculation with Pst DC3000 showed a significantly reduced chlorosis phenotype (compared to wild-type Col-0), while co-inoculation with Pst DC3000 and cytochalasin-d resulted in the elicitation of a pronounced disease phenotype. Co-inoculation of the kinesin mutant with Pst DC3000 and jasplakinolide showed a marked reduction in disease symptoms. D, Bacterial growth assays of Pst DC3000 in wild-type Col-0 and the kinesin mutant. Pst DC3000 strains were inoculated at a concentration of 3 × 107 cfu ml−1. Bacterial growth assays were performed two times with similar results. Error bars, representing mean ± se, were calculated from three (n = 6) technical replicates of two independent biological repeats. In planta pathogen growth was enumerated based on cfu per cm2 plant tissue. Statistical significance was assessed using a Student’s t-test. E, The actin-stabilizing and barbed-end binding agents, jasplakinolide and cytochalasin-d, respectively, do not affect the in planta growth of Pst DC3000 in wild-type Col-0 or the kinesin mutant. Five-week-old wild-type Col-0 leaves were co-infiltrated with cytochalasin-d or jasplakinolide and Pst DC3000 (2 × 105 cfu ml−1), and bacterial growth was enumerated at 3 dpi. Bacterial growth assays were performed two times. Error bars, representing mean ± se, were calculated from three (n = 6) technical replicates of two independent biological repeats. Statistical significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA, Tukey test; P < 0.01. CD, cytochalasin-d; f.w., fresh weight; Jasp, jasplakinolide; Mock, MgCl2.