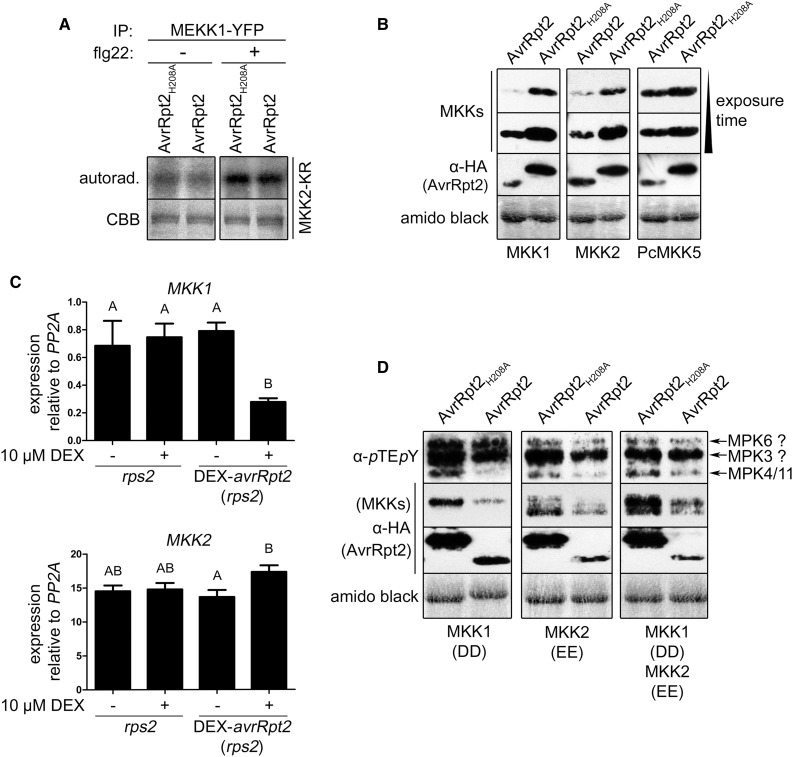
Figure 9.
Possible mechanism for the suppression of MPK4/11 activation by AvrRpt2. A, MEKK1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) with GFP-trap beads from protoplasts (rps2) coexpressing MEKK1-YFP and AvrRpt2-HA variants (+ or − 100 nm flg22 treatment, 1 h) and used to phosphorylate recombinant MKK2-KR as a substrate in radioactive in vitro kinase assays. autorad., Autoradiography; CBB, Coomassie Brilliant Blue stain. B, Effect of (in)active AvrRpt2 on the levels of Arabidopsis MKK1/MKK2 (or the parsley MKK5 [PcMKK5] as a control) in protoplasts (rps2). Western blots were successively probed with anti-c-myc (for PcMKK5) and anti-HA (for MKKs and AvrRpt2 variants) antibodies. C, Effect of AvrRpt2 on MKK1/MKK2 transcript levels. DEX-avrRpt2 (in the rps2 background) and rps2 control plants were treated with 10 µm DEX (16 h) to induce AvrRpt2 expression, and the expression of MKK1/MKK2 was analyzed by real-time PCR. Letters indicate statistically significant differences (n = 4; one-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test after log2 transformation of the data). The experiment was repeated four times with similar results. D, Effect of AvrRpt2 on the MPK4/MPK11 phosphorylation induced by constitutively active MKK1T218D,S224D (DD) and/or MKK2T229E,T235E (EE) in protoplasts (rps2). MKK levels were analyzed by immunoblotting as described in B. Experiments A, B, and D were repeated twice with similar results. Amido Black staining (B and D) after immunoblotting (showing the large subunit of Rubisco) was used to demonstrate equal loading.