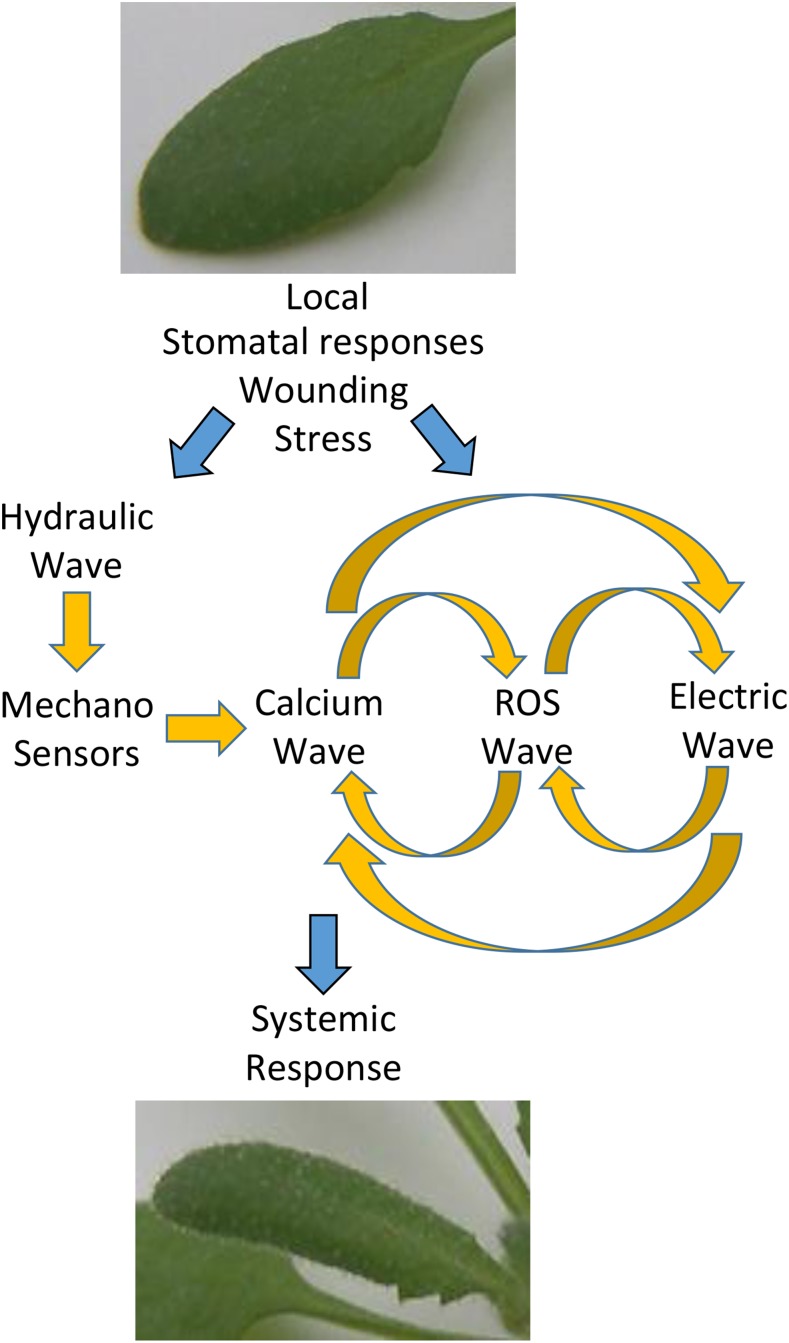
Figure 3.
Integration of the different waves that mediate rapid systemic signaling during SAA. Local stimuli are shown to trigger the ROS/calcium/electric wave, as well as a hydraulic wave that in turn triggers the calcium wave via mechano-sensors. The calcium and ROS waves are shown to be linked (possibly via RBOH and TPC1/CPK function), the ROS and electric waves are shown to be linked (possibly through RBOHD and GLR function), and the calcium and electric waves are shown to be linked (possibly via channels such as GLRs or similar). The different waves are shown to mediate the propagation of each other and to trigger a response in the systemic tissue.